Key Differences Between Competitive and Market Intelligence


Key Takeaways:
Poor procurement decisions often result from confusing competitive intelligence (CI) with market intelligence (MI), treating them as interchangeable despite their distinct roles.
This confusion leads to costly errors: distorted strategies, wasted resources, missed opportunities, weakened competitiveness, and vulnerable supply chains.
This guide clarifies CI vs. MI differences, showing when and how to use each to enhance strategy, strengthen decisions, and stay ahead of rivals and market changes.
Competitive intelligence (CI) is the process of gathering and analyzing information about your competitors and industry marketplace to inform strategic business decisions and gain a competitive advantage.
Reflecting its strategic value, 90% of Fortune 500 companies already use CI to gain a competitive edge.
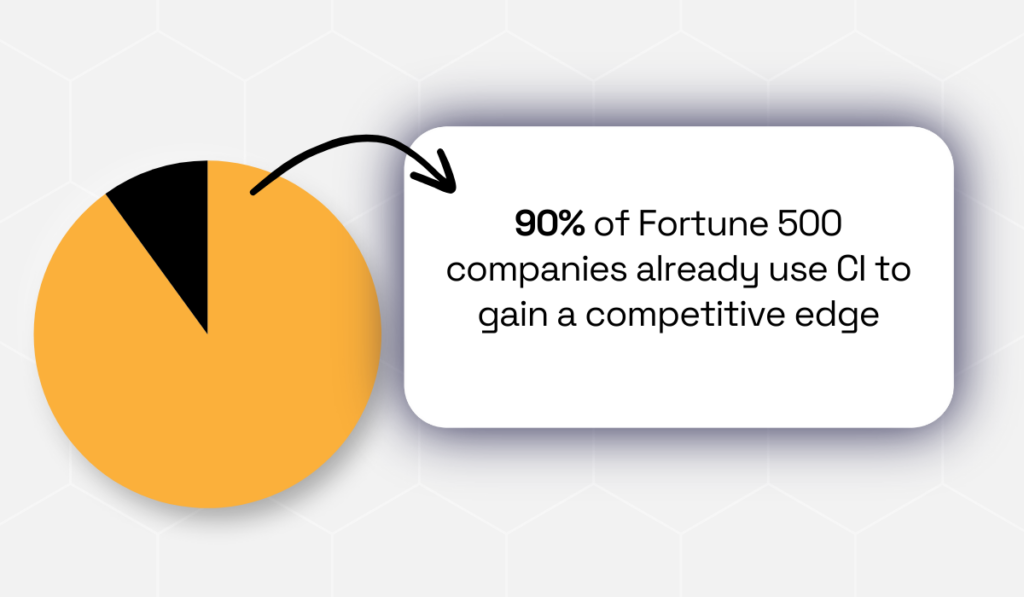
Illustration: Veridion / Data: Emerald
Thus, CI has become a core capability for organisations that want to lead, not follow.
This widespread adoption is further underscored by the projected growth of the global CI market, which is expected to reach $82 million by 2027.

Illustration: Veridion / Data: Fortune Business Insights
Crucially, while CI does consider the industry context, its main focus is on understanding specific rivals rather than the market as a whole.
In practice, this means researching a competitor’s products, pricing, marketing, and overall strategies.
The intent is to uncover their strengths and weaknesses, identifying gaps your business can exploit to outperform them.
For example, you might monitor a rival’s product launch or marketing campaign to see what resonates with customers, or analyze their pricing and distribution strategies.
This may sound like CI is illegal espionage—but it’s not.
Competitive intelligence relies on ethical sources like press releases, competitor websites, financial reports, advertisements, industry publications, and social media profiles.

Source: Veridion
The goal of competitive intelligence is to improve your competitive position by understanding everything possible about key competitors.
Armed with this intelligence, you can make more informed decisions about how to compete for market share.
This advantage extends to procurement.
By analyzing competitors’ supply chains, you can uncover how they optimize costs, manage supply chain risks, or negotiate better terms with suppliers.
Studying a rival’s sourcing strategies might reveal approaches such as:
These insights can inform your own procurement strategy, helping you reduce risk, improve supplier relationships, and gain a competitive edge.
Ultimately, CI provides the detailed intelligence you need to understand competitors deeply and strategically outmanoeuvre them.
Market intelligence (MI) refers to gathering and analyzing comprehensive market data to understand the overall industry, market trends, and customer needs.
Unlike CI, which looks only at rivals, MI takes a broader view.
It examines overarching market dynamics, customer preferences, and macroeconomic factors.
This includes analyzing market size and growth potential, customer demographics, the impact of emerging technologies, and regulatory changes.
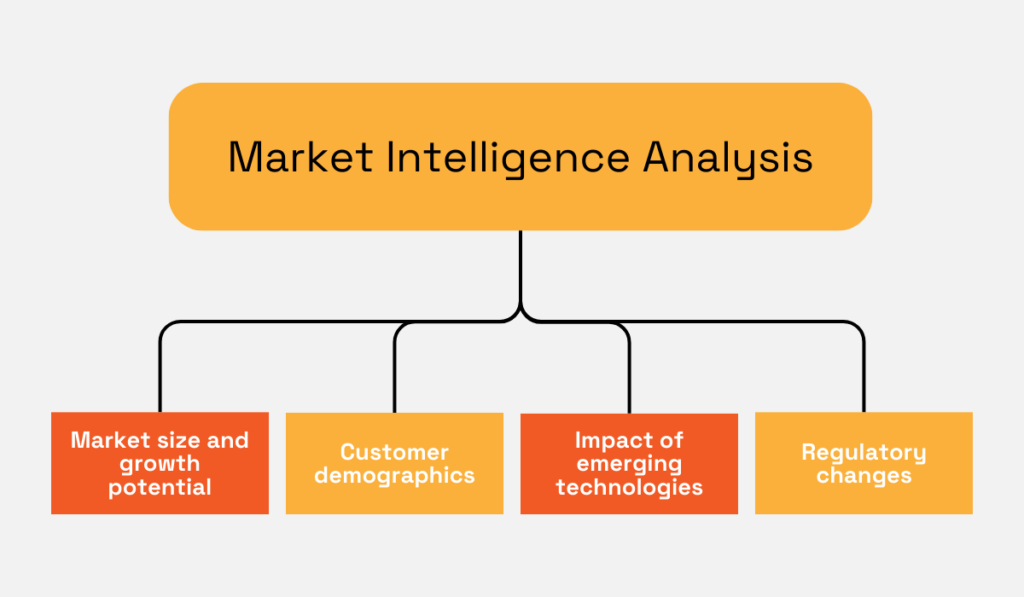
Source: Veridion
For example, MI can reveal shifts in customer demand, highlight new opportunities, or identify risks that could affect your supply chain.
The strategic value of MI is driving substantial investment in analytics tools.
The global big data analytics market, which underpins much of MI, was valued at $307.52 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach $962 billion by 2032, underscoring the growing importance of these capabilities for modern businesses.
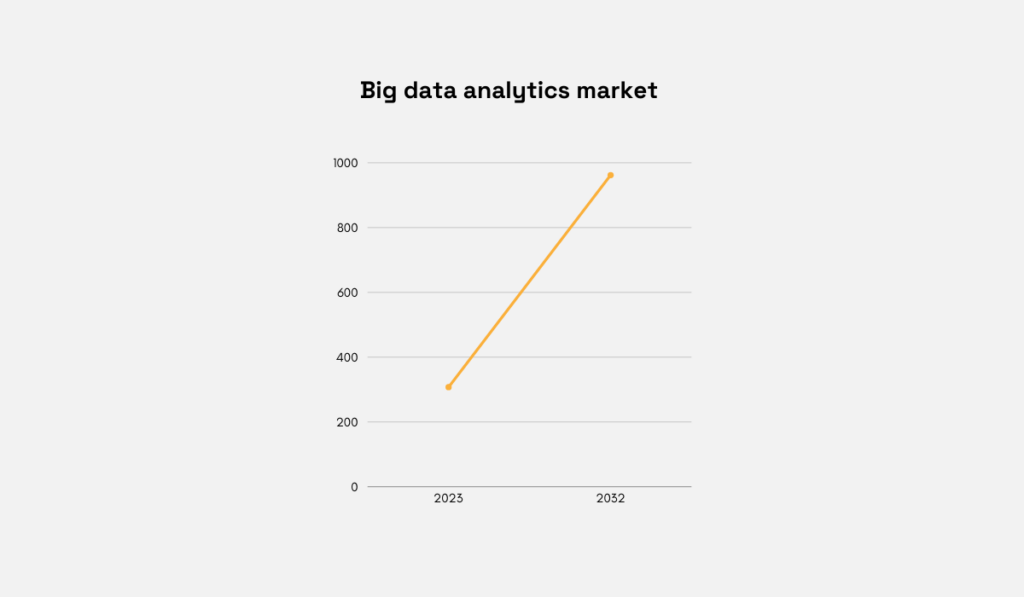
Illustration: Veridion / Data: Fortune Business Insights
Within procurement, MI helps track supply and demand fluctuations, raw material availability, and price volatility.
These insights allow procurement teams to make better sourcing decisions, anticipate risks, and align purchasing strategies with market realities.
For instance, a 2024 Deloitte survey shows that 92% of CPOs are planning or assessing generative AI capabilities, highlighting the role of technology in improving decision-making.
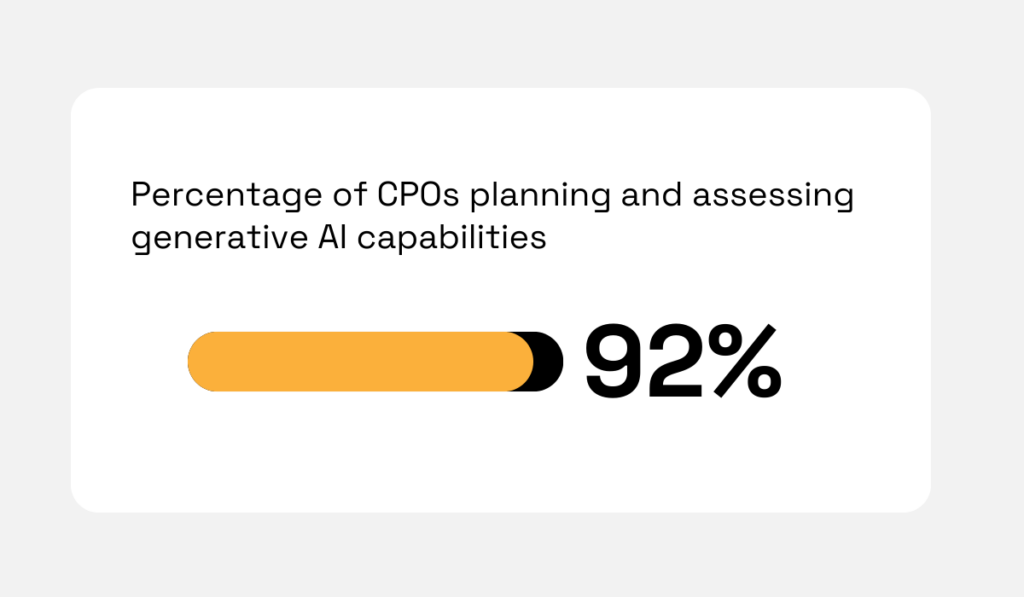
Illustration: Veridion / Data: Deloitte
This widespread exploration signals that AI-driven automation and data analysis are fundamentally transforming procurement market intelligence.
Now, successful market intelligence compiles and synthesises data from diverse sources, including:
By analyzing these inputs, businesses can answer critical strategic questions, such as:
By providing clear answers to these questions, market intelligence delivers usable information.
It illuminates the key market drivers and underlying customer behaviours that should shape your procurement strategy.
Too often, competitive and market intelligence are used interchangeably, creating costly confusion.
This misunderstanding can lead to misallocated resources, flawed strategies, and missed opportunities.
While both disciplines rely on data gathering and analysis, their objectives differ fundamentally.
Jayde Phillips, Senior Manager of Strategy and Market Intelligence at Egencia, gives a clear distinction between the two:

Illustration: Veridion / Data: Competitive Intelligence Alliance
In other words, competitive intelligence focuses on understanding specific rivals—what they are doing, how they operate, and where their strengths and weaknesses lie.
CI answers the question: “What are our competitors doing?”
For example, monitoring a supplier’s bids, pricing tactics, or innovation roadmap can reveal opportunities to gain a strategic advantage.
Market intelligence (MI), on the other hand, looks at the broader market.
It tracks trends, supply and demand fluctuations, customer behavior, and emerging risks.
MI answers the question: “What’s happening in our market?”
For instance, a sudden 20% increase in lithium prices can cascade into supply chain disruption, higher costs, and production delays.
MI helps organizations anticipate these changes and plan accordingly.
Below is a recap of their differences:
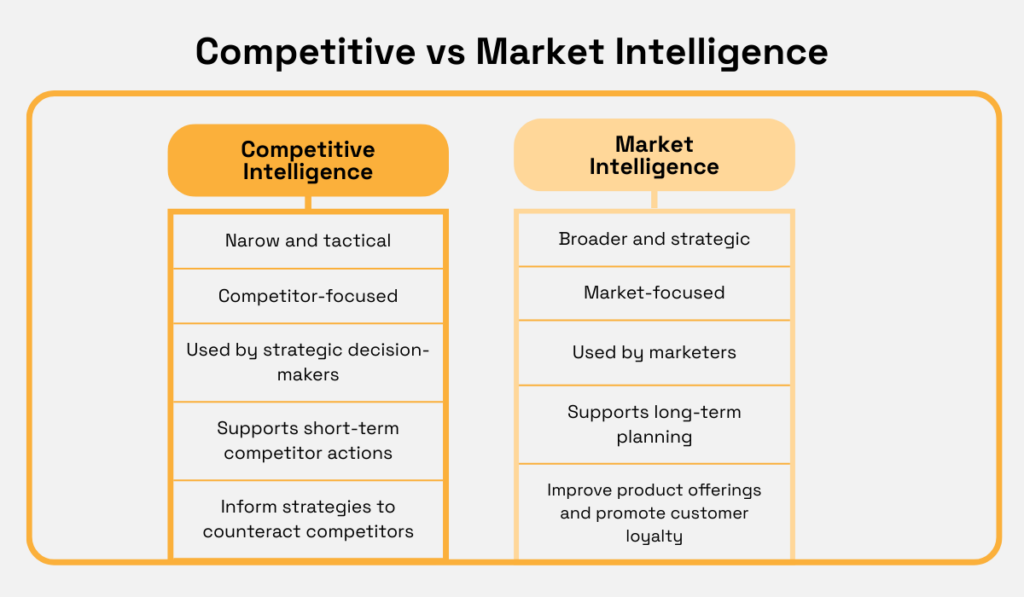
Source: Veridion
By understanding these differences, businesses can better frame the type of intelligence they need and approach decision-making with a clearer perspective.
Competitive intelligence (CI) delivers the greatest advantage when you need to anticipate and counter specific competitor actions.
In sales and proposals, CI is especially valuable for preparing major contract bids or RFP responses.
By analyzing how rivals structure their offers, you can develop standout proposals, highlight unique strengths, and neutralize competitors’ perceived advantages.
Small improvements in proposal quality matter.
The industry average RFP win rate sits at 45%, so CI-informed advantages in positioning or pricing can lift your odds of winning.
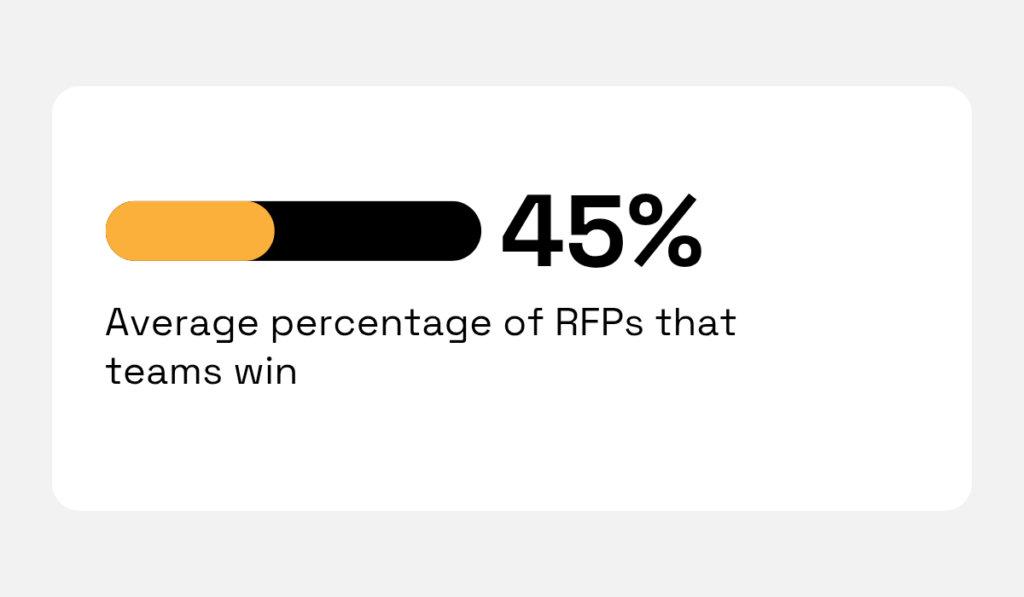
Illustration: Veridion / Data: Loopio
Similarly, before launching marketing campaigns or positioning new products, use CI to see how competitors market similar offerings.
This helps you to differentiate your approach and exploit gaps they have overlooked.
In product development, analyzing competitor features, innovations, and pricing shifts through CI provides benchmarks.
Reverse-engineering a rival’s product can also give your team a useful starting point for improvement.
Within procurement, CI allows you to dissect competitors’ supply chains and sourcing strategies.
If a rival secures better pricing or faster delivery, CI can reveal how they did it, guiding negotiation tactics, supplier diversification, and cost optimization.
It also helps set pricing strategies by identifying where you can adjust margins to win key contracts.
Beyond strategic advantages, CI helps mitigate risk by revealing competitors’ missteps, so you can avoid similar pitfalls.
Continuous monitoring ensures you react swiftly to market moves, such as product launches or expansions.
Ultimately, CI provides the granular insights needed to act decisively across sales positioning, proposal development, product strategy, and procurement.
Michael Porter, Professor of Competitive Strategy at Harvard Business School, says:

Illustration: Veridion / Data: Toolshero
That’s precisely the point of CI: it reveals the gaps to help you find where you can be different from your competitors.
Market Intelligence (MI) becomes essential when procurement decisions demand a comprehensive, real-time understanding of external market dynamics.
In fact, 95% of decision-makers believe better access to information would improve their choices.

Illustration: Veridion / Data: Amplyfi
And in 2025, the ability to gather, analyze, and act on intelligence in real-time becomes the defining factor between market leaders and followers.
Supplier discovery and evaluation is a prime application of MI.
When identifying new suppliers across global markets, MI provides the scale and depth needed to uncover qualified partners beyond your existing network.
This ensures you can assess capabilities, capacity, and alignment with your business objectives before engagement.
Market intelligence is also indispensable for proactively assessing broad market shifts such as commodity price volatility, supply chain disruptions, or emerging regulatory risks.
It enables you to adjust sourcing strategies before impacts materialize.
This information-driven approach aligns perfectly with the industry’s trajectory.
Sarah Barnes-Humphry, host of the Let’s Talk Supply Chain™ podcast, emphasizes this in her podcast:

Illustration: Veridion / Data: Podcast Opensap
This information-driven approach is fundamental when evaluating expansion into new categories or geographies.
Here, MI delivers the essential trend analysis and growth indicators needed to validate opportunities and allocate resources.
This external, high-volume data is particularly vital when your decisions rely on continuous market scanning rather than reactive intelligence.
For example, monitoring supplier financial health indicators or tracking sustainability regulations across regions demands consistent, automated insights.
Solutions like Veridion, built for enterprise-grade market intelligence, meet these demands.
Source: Veridion
By applying advanced machine learning to process large online data streams, Veridion converts unstructured information into structured, continuously updated intelligence on millions of global suppliers.

Source: Veridion
Veridion automates the heavy lifting of market scanning, empowering you with the intel needed for vendor sourcing and supply chain management.
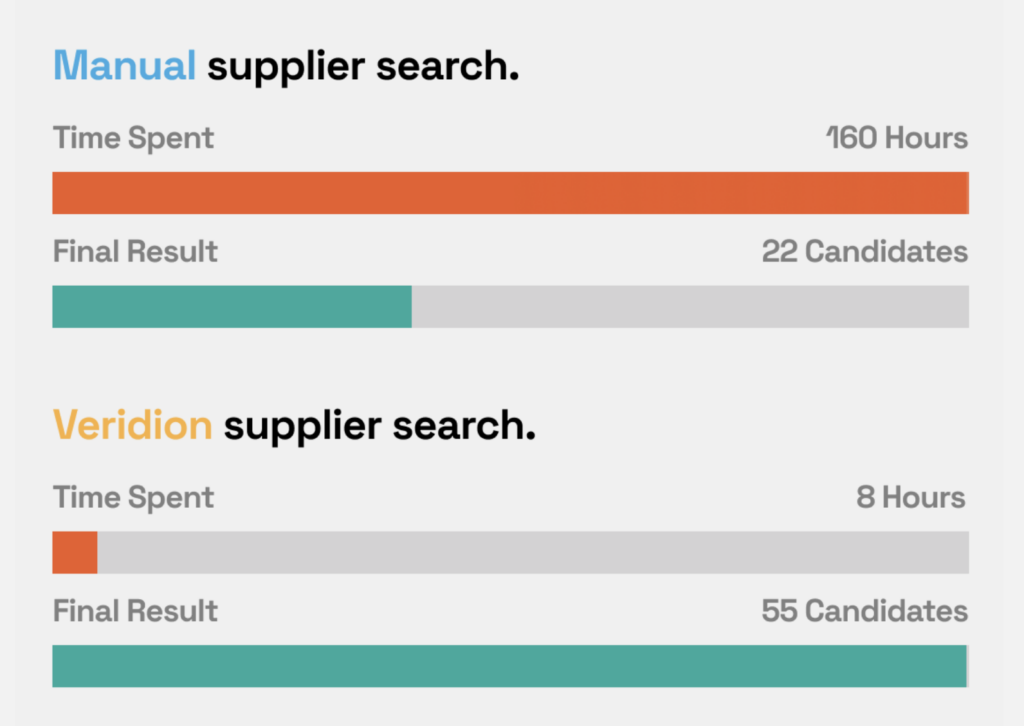
Source: Veridion
Below are three more ways in which Veridion’s market intelligence helps companies:
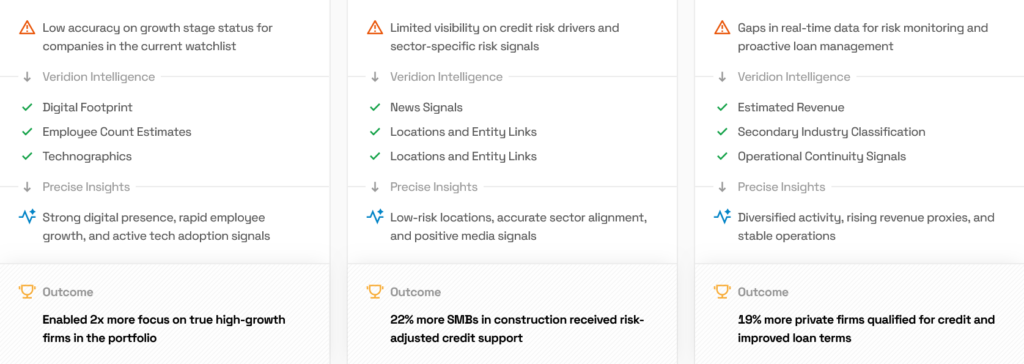
Source: Veridion
In the end, market intelligence is most valuable when decisions require a real-time, comprehensive understanding of the market, such as identifying new suppliers, anticipating risks, or evaluating expansion opportunities.
Confusing CI and MI drains resources, distorts strategy, and blindsides you to opportunities, which erodes your competitive edge.
The solution is clarity:
Use CI to analyze competitor moves in bids, pricing, and supply chains, and MI to anticipate market shifts, risks, and global disruptions.
They complement each other and can give you an unmatched strategic vision.
Applied correctly, both CI and MI improve supplier negotiations, support market entry decisions, and drive measurable savings, better positioning, and more efficient operations.