AI in Insurance Underwriting: Key Insights


Key Takeaways:
Can AI and machine learning accelerate the entire underwriting process while keeping decisions accurate and compliant?
This question is driving executives and leaders to seek smarter, scalable solutions.
If you want to see what artificial intelligence can do for your operations, you’re in the right place.
This article explores how AI is transforming underwriting, the measurable benefits it can bring, and its key use cases.
The current state of the AI market within the insurance underwriting sector is looking very promising.
In fact, data from Cons&Insights estimates that AI in underwriting will see strong growth in the coming years.
They predict the market will move from its size of 2.30 billion USD in 2024 to more than double that figure by 2033.

Illustration: Veridion / Data: Cons&Insights
This expansion is natural, as AI adoption in the insurance industry has moved beyond the phases of simply experimenting and development.
Today, it is in active deployment for a significant number of insurance companies.
For example, in their 2025 annual survey on AI and insurance technology, Conning analyzed how C-Suite executives are approaching this technology.
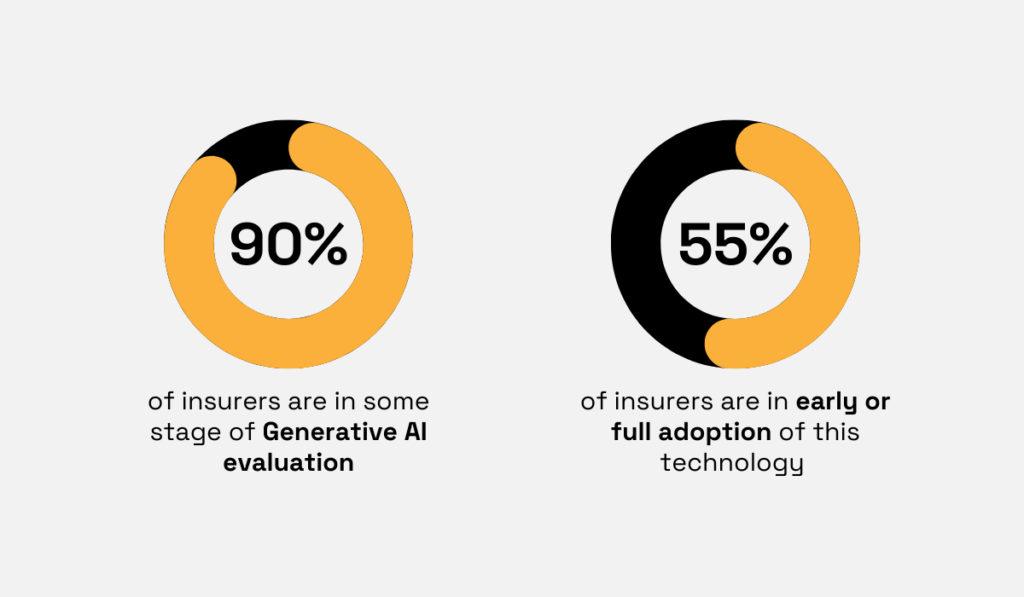
Illustration: Veridion / Data: Conning
As you can see, over half of insurers have already adopted AI, and almost all organizations are currently evaluating it.
This suggests that the majority of the industry will soon follow.
This momentum is driven by AI’s ability to process massive volumes of both structured and unstructured data with speed and consistency that human-led processes simply cannot match.
This perspective is echoed by the head of insurance research at Conning, Scott Hawkins, who stated that AI can dramatically reduce complexity for teams in an increasingly data-diverse space.

Illustration: Veridion / Quote: Insurance Thought Leadership
Going forward, AI is expected to further reshape underwriting.
As data availability improves and model sophistication grows, insurers will leverage these tools as part of continuous risk assessments, with faster decision cycles and more dynamic pricing models that reflect real-life conditions.
In short, the technology is quickly graduating from a theoretical advantage to the new standard for underwriting.
Before we look at specific use cases, it helps to understand what AI actually brings to the table.
As you will see, the benefits are practical and can affect the entire underwriting process.
Let’s walk through four key advantages that make AI valuable for underwriting teams.
Compared to manual data entry and analysis, AI can significantly expand what underwriters can actually work with.
A core benefit of these systems is that they can ingest and interpret large quantities of structured data.
In the case of insurance underwriting, this means processing massive amounts of information like financial statements, claims histories, and policy records, and delivering organized results in minutes rather than days.
However, where this technology really proves useful is with unstructured data.
This includes things like emails, PDFs, photographs, handwritten notes, and inspection reports.
Traditionally, collecting and analyzing unstructured data has been difficult as it requires underwriters to manually read, interpret, and enter information into usable formats.
That takes time and introduces errors.
That’s where agentic AI solutions like V7 Go come in.
This tool can easily process images and do efficient data extraction from handwritten documents, scanned forms, and other non-standard inputs.
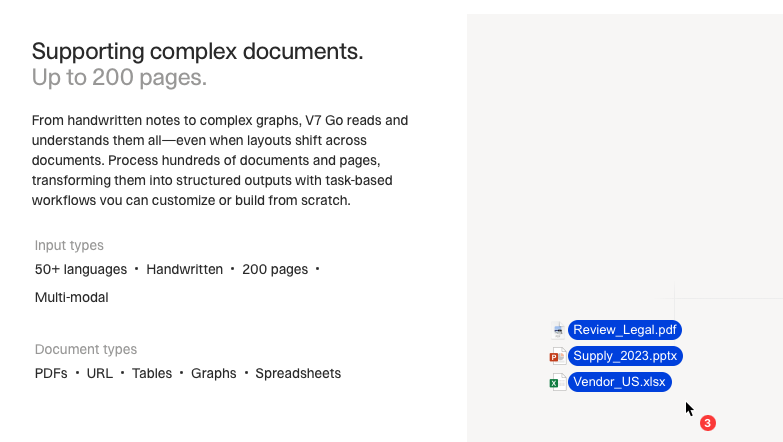
Source: V7 Labs
Previously, underwriters often had to make decisions based on incomplete information simply because gathering everything took too long.
But AI helps reduce this reliance on partial data.
It unlocks efficiency, but more importantly, it gives underwriters a more comprehensive and accurate view of insurance risk, which leads to better pricing and fewer surprises down the line.
As we just explained, AI can provide significant support or even replace many human-led, manual processes entirely.
This matters because underwriters spend a surprising amount of time on tasks that aren’t actual underwriting.
According to Capgemini, a large portion of underwriters’ working hours goes toward operational and administrative tasks.
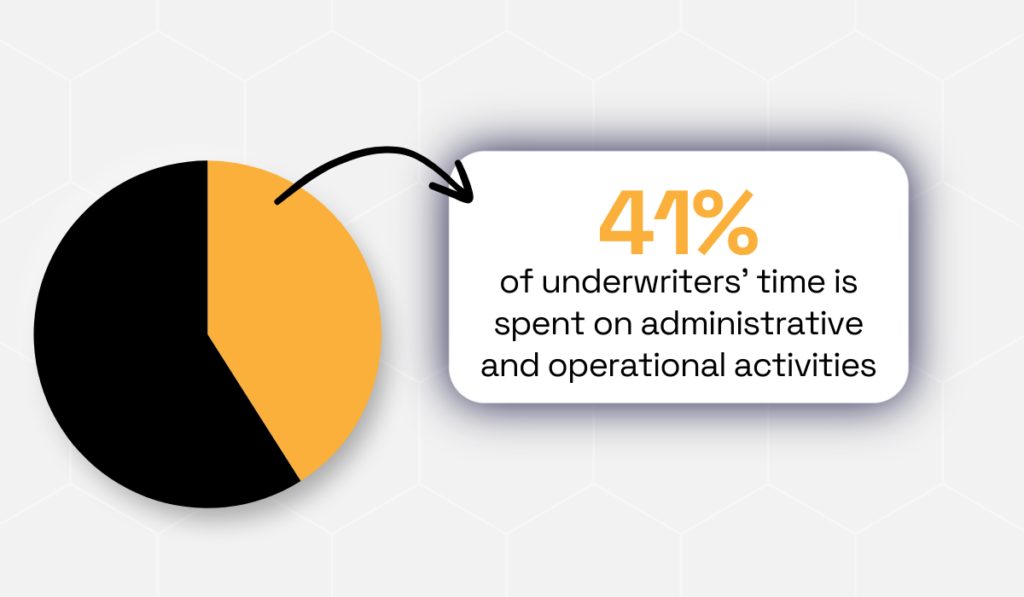
Illustration: Veridion / Data: Capgemini
Luckily, AI-powered automation excels at these repetitive, rule-based tasks.
Document review, data collection, and validation are good examples. Even initial risk scoring and preliminary reviews can be handled by AI systems.
Of course, a human will still check the output and make final decisions.
But this approach saves considerable time since the bulk of the work gets done in minutes instead of days.
The ultimate goal goes even further.
Peter Zaffino, Chairman and CEO of American International Group, one of the world’s largest insurance companies, has spoken about using AI for the entire end-to-end underwriting process.

Illustration: Veridion / Quote: CM
Zaffino and Claude Wade, AIG’s executive VP and Chief Digital Officer, have discussed utilizing AI agents for everything from data ingestion at the start of the underwriting process, all the way to calculating propensity to bind at the end.
That level of automation represents a major shift in how underwriting departments could operate.
Another crucial area where artificial intelligence supports insurance underwriting is fraud detection and prevention.
We call this area crucial because, according to Cifas’ research, false insurance applications are growing.
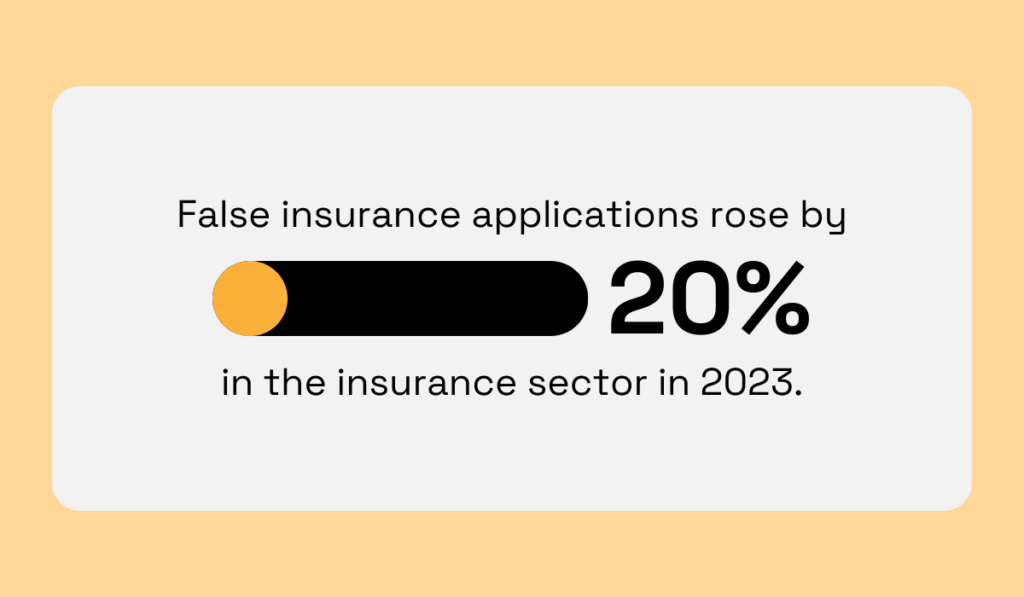
Illustration: Veridion / Data: Cifas
With fraud constantly evolving and its cost increasing, human experts need all the support they can get.
AI can identify anomalies and behavioral patterns that may not be obvious through manual review.
For example, an AI fraud detection model might find that an applicant’s claimed business revenue doesn’t match typical patterns for their industry size and location, flagging it for further investigation.
The best part?
This analysis can happen at scale and just get better over time.
Applications can get flagged as inconsistent or suspicious in real time, prompting a human underwriter to take a second look.
The AI models learn from human verification, drawing from the confirmed fraud cases and their specific details.
This means they catch similar situations more effectively when they appear again.
So, if a human underwriter were to let something slip by mistake, AI would be there to help with data from thousands of fraud instances at its disposal.
It’s no wonder, then, that 62% of insurers believe AI/ML tools are elevating underwriting quality and reducing fraud.
Together, human judgment and AI analysis create a stronger defense against these fraudulent activities.
Finally, the use of AI in underwriting can have a downstream impact on claims processing.
Let’s consider the case of Great American Insurance, which implemented an AI tool called SortSpoke.

Illustration: Veridion / Data: SortSpoke
The company had been struggling with manual document processing.
After implementing the AI solution, they gained an enormous efficiency boost while maintaining fully accurate documentation.
This directly impacts claims processing in two ways:
First, AI-powered claims verification can review claims faster, especially when the underlying policy data is already clean and well-organized.
Second, better document quality during underwriting means cleaner risk profiles that claims adjusters can reference later.
Speaking of risk, Great American’s underwriters also received AI support in extracting and processing unstructured data, which would lead to more complete risk profiles from the start.
So, when a claim comes in, adjusters have better information about what was actually covered and why.
Ultimately, claims processing and underwriting are tightly connected.
Decisions made during underwriting shape how smoothly claims get handled months or years later.
By improving data quality and risk assessment upfront, AI in underwriting creates benefits that extend well beyond the initial policy decision.
The benefits we covered represent just a few ways AI supports underwriting teams.
There are many more specific applications worth exploring.
Now, we’ll look at some concrete use cases that show how these technologies work in practice.
We mentioned AI supporting risk assessment as one of the key benefits, but let’s examine this use case more closely.
Consider a platform like Veridion, which uses its AI and machine learning powered data engine to collect verified and curated business intelligence.

Source: Veridion
Veridion covers over 130 million companies across 250 countries, with more than 300 company data attributes in each profile.
This data includes key information for performing underwriting assessments, such as
When underwriters work with potentially incomplete applicant data, they can use Veridion’s Match & Enrich service, which fills in missing company information by matching records against Veridion’s comprehensive database.
Source: Veridion on YouTube
In fact, full business profiles can be completed in minutes, replicating processes done in days or weeks by human underwriters.
When core underwriting risks are identified, teams can focus on the more nuanced aspects of risk evaluation and create complete risk profiles.
Based on these risk assessments and the wealth of data that AI can analyze, underwriting can become even more personalized.
We’re talking about granular policy pricing at the individual policy level, not just broad category averages.
That is possible with the help of machine learning models capable of accounting for operational behavior, location-specific risks, and historical trends simultaneously.
They process all these factors together and find relationships that would be impossible to calculate manually.
As a concrete example, consider NAIC’s research findings.
Their data shows that almost half of insurers already use AI or machine learning for calculating rates, either fully or for certain aspects.
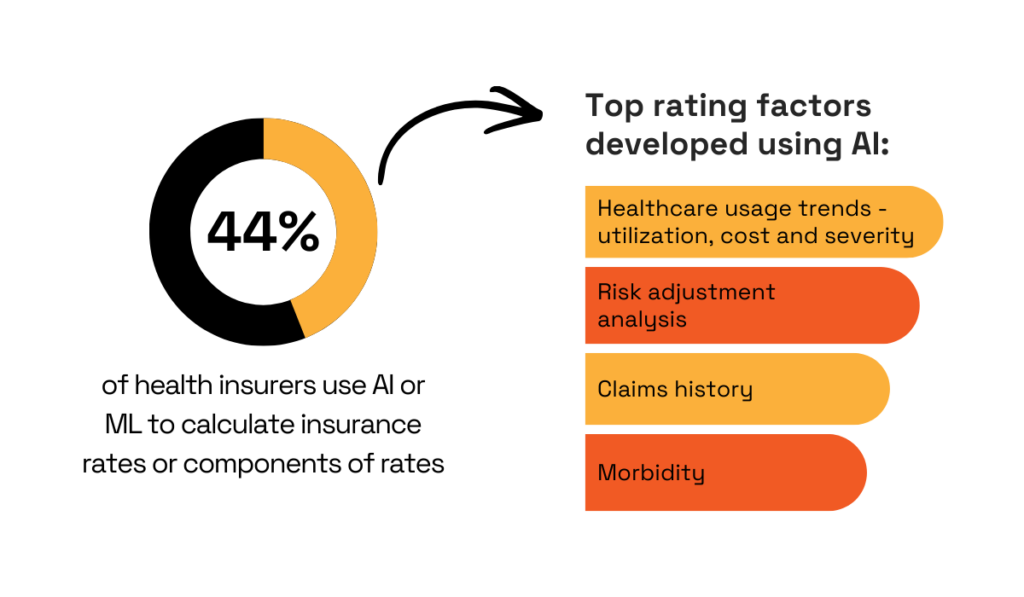
Illustration: Veridion / Data: NAIC
The top rating factors processed through these systems are complex and interlinked.
They include healthcare usage trends, risk adjustment analysis, claims history, and morbidity data.
Analyzing how all these variables interact with each other is only possible with AI because the calculations involve thousands of data points across multiple dimensions at once.
This approach helps insurers move beyond using traditional ways to determine premiums.
Instead, they can offer highly specific, tailored pricing that reflects actual risk.
The result benefits both sides. Insurers price more accurately, and customer satisfaction rises as they pay fairer premiums based on their real circumstances.
When it comes to property, commercial, mortgage, and other asset-based insurance underwriting, AI assists greatly with valuation.
Just like with the previous examples, AI solutions can pull and integrate asset data such as cost estimates, depreciation models, geospatial data, and even broad market signals.
These models then combine all inputs to generate accurate, current valuations without requiring manual property valuation.
Consider the following snippet commenting on CAPE’s Home Insurance Property Intelligence solution.

Source: Moody’s
Combining satellite imagery and computer vision alongside signals like natural disaster occurrence, public records, and other risk factors, it can accurately assess millions of properties in moments.
This data-backed and automated valuation reduces subjectivity and ensures consistency across policies.
Ultimately, valuation directly affects risk assessments and premium calculations.
So, when asset values are accurate from the start, insurers avoid both underpricing risky properties and overcharging for well-maintained ones.
Finally, AI models can support traditional actuarial analysis as well.
This capability stems from these models’ ability to process large datasets more efficiently than conventional statistical methods.
As Ronald Richman, founder and CEO of Insure AI and a recognized researcher in actuarial deep learning, explains, these tools can then find complex nonlinear relationships in this data.
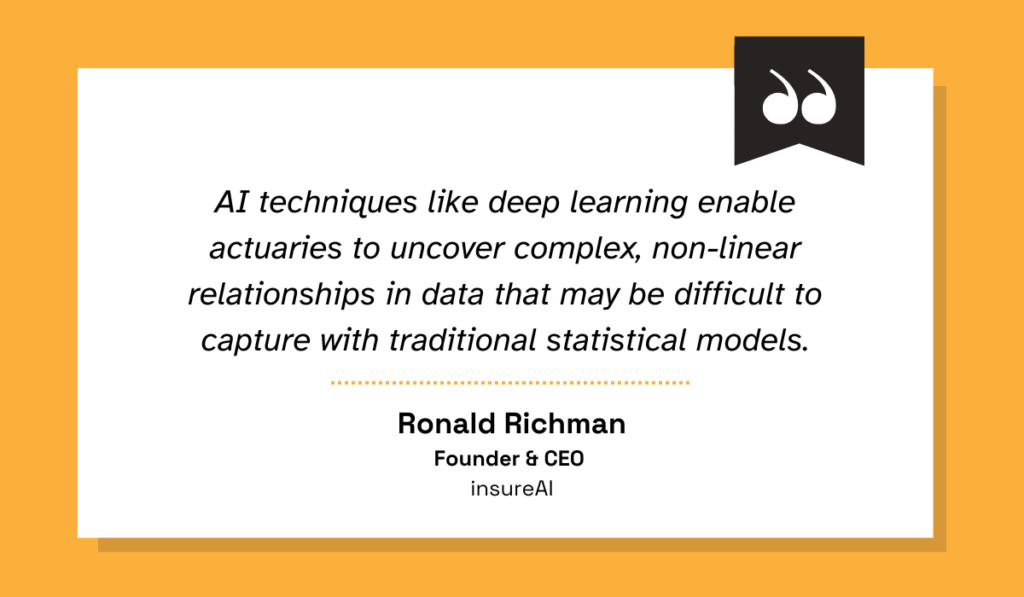
Illustration: Veridion / Quote: CAS
For example, an AI model analyzing auto insurance data might discover that claim frequency for drivers aged 25–30 increases sharply only when three separate factors occur together.
Compared to that analysis, traditional linear models might evaluate each factor independently and miss this combined effect entirely.
These hidden patterns help actuaries build more accurate pricing and reserving models.
In summary, AI enhances actuarial work by uncovering insights buried in complex data.
It processes more variables and tests more combinations than manual analysis could achieve.
Actuaries still provide essential expertise and judgment, but AI gives them better tools to identify risks and set appropriate reserves.
That covers the essentials of AI in insurance underwriting.
We explored how these technologies assess risk, speed up decision-making, and improve accuracy across your processes.
Hopefully, you now have a clearer picture of where AI fits into modern underwriting workflows.
Consider starting with one area where automation could reduce your team’s manual workload, then expand from there as you see results.