Big Data In Procurement: A Quick Guide

Procurement departments in large enterprises are certainly no strangers to managing a lot of data from multiple sources, such as transactional records, supplier databases, market intelligence reports, and internal performance metrics.
Therefore, it’s only logical they should embrace the power of big data analytics and tools in procurement.
From increased procurement efficiency and improved decision-making to quicker supplier sourcing, effective spend analysis, and better relationship management, the transformative potential of big data cannot be overstated.
In this quick guide, we’ll cover what big data is, how it’s used in procurement, and what key technologies and methods you can use to incorporate it into your workflows and processes.
To better understand the role of big data in procurement, let’s first cover what it means.
According to Google Cloud:
“Big data refers to extremely large and diverse collections of structured, unstructured, and semi-structured data that continues to grow exponentially over time”.
Such data collections are compiled from various internal and external sources, such as business transaction systems, customer databases, social networks, clickstream logs, and other public or proprietary records.
Big data is typically described by the three Vs (volume, variety, velocity) with three more Vs added for more precise characterization (veracity, value, variability).
You can see all the six Vs of big data here.

Illustration: Veridion / Data: Tech Target
Overall, big data is an umbrella term for very large and diverse datasets. Some say it doesn’t refer to data itself but to technologies used for the treatment of that diverse and complex data.
Traditional data management systems usually can’t store, process, and analyze such big datasets, so specific technologies and tools have emerged to help companies extract value from these large and complex datasets. We will cover them later on.
Big data is highly relevant in modern procurement processes, and that brings us to our next section.
The versatility of big data empowers companies to enhance many facets of the procurement process, fostering a comprehensive and data-driven approach.
In this section, we’ll examine how procurement specialists can leverage big data in the four key use cases: supplier sourcing, spend analysis, supplier relationship management, and demand forecasting.
Big data is essential for supplier identification, evaluation, and selection (or, in one word, sourcing), which are arguably the most important steps for successful procurement.
That said, sourcing suppliers that best meet your company’s needs and strategic goals is often a daunting, time-consuming, and largely manual process, which is supported by the McKinsey article:
“On average, it takes about three months to complete a single supplier search, with a sourcing professional logging more than 40 hours of work—and yet able to consider only a few dozen suppliers from a total population of thousands.”
The same article claims that organizations can cut the time needed to find the right suppliers by 90% or more with the help of artificial intelligence (AI) tools, enabling them to find new suppliers in days instead of months.

Source: McKinsey
To explain how AI-powered big data tools can produce these amazing results, let’s examine one such supplier-sourcing solution, our own Veridion.
Veridion comes as an application programming interface (API) that allows for quick and easy integration with other software applications your company is using, such as enterprise resource planning (ERP), e-procurement, and supply chain management systems.
Veridion’s proprietary search API comes with access to the most complete, weekly updated, global supplier database with over 80 million entries covering nearly 200 million business locations.
Source: Veridion
In practical terms, this means you can use the search API and the database to quickly and easily discover potential suppliers that fit a variety of your procurement criteria.
For example, if you were looking for a new raw coffee supplier, your search could include criteria like geographic location, sustainable and ethical sourcing practices, production capacity, and industry certifications.
Moreover, Veridion’s supplier database uses proprietary, AI-based machine-learning models that go through billions of websites and petabytes of data weekly, ensuring the most complete, reliable, and up-to-date search results.
In a demo video showing how a pharmaceutical company can find microcrystalline (MCC) suppliers using Veridion, Drew Doherty explains that:
“A Veridion query typically lasts under five seconds. As you can see, Veridion’s API found 175 companies, while competing solutions only found 32 suppliers. Our clients often find such differences after working with our data.”
Therefore, an AI-powered supplier sourcing tool like Veridion can not only drastically cut the time needed for the initial supplier search but also produce more precise and comprehensive results.
From there, the identified suppliers can be further evaluated based on specific performance metrics, compliance with industry standards, and alignment with your company’s strategic goals, allowing for a thorough and data-driven supplier selection process.
To summarize, big data tools minimize the time and resources invested in supplier sourcing by providing accurate and data-rich supplier search results, enabling organizations to transform their strategic sourcing processes.
Another area where big data and associated tools fit like a glove is spend analysis.
That’s not surprising given that the purpose of spend analysis in procurement is to gain a comprehensive understanding of an organization’s expenditures, vendor relationships, and purchasing patterns.
Empowered by the obtained insights, organizations can identify cost-saving opportunities, evaluate and enhance supplier performance and compliance, mitigate risks, and generally make better-informed, data-driven procurement decisions.
As such, spend analytics encompass collecting, cleansing, enriching, categorizing, and analyzing spend data from both internal and external datasets to examine the following elements and answer their related questions:

Source: valQ
Given the above, it’s clear that big data tools, with their processing capacity and advanced analytics, are ideal for enhancing all elements of procurement spend analysis that traditionally rely on internal datasets of limited scope.
In other words, big data technologies can:
Overall, utilizing big data tools in spend analysis enhances the quality and results of traditional approaches and paves the way for more informed, data-driven decisions in procurement.
By utilizing big data tools to track and analyze supplier performance, compliance data, and market trends, organizations can make informed decisions to improve their supplier relationship management (SRM).
External big data platforms can address one of the major issues in SRM, which is not being aware of crucial factors affecting the supplier’s performance, such as financial stability, material sourcing issues, or compliance with industry standards.
In fact, a 2020 study showed that misinformation about suppliers is a common problem for procurement specialists:
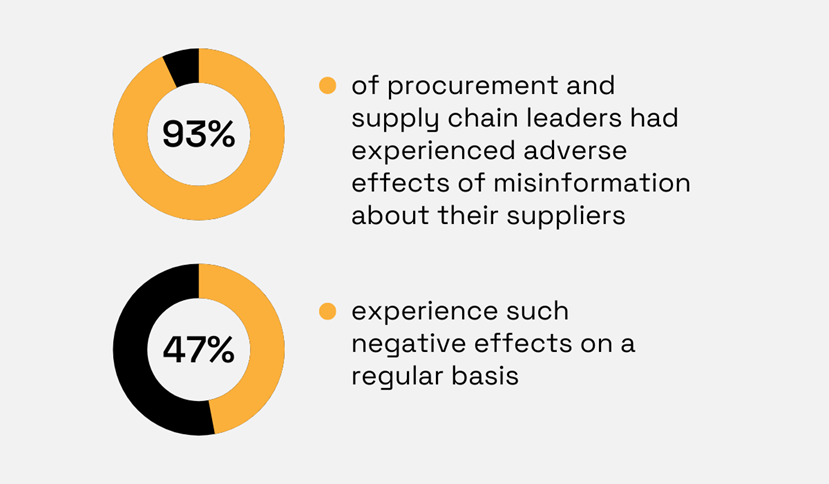
Illustration: Veridion / Data: TealBook
The above data shows that monitoring supplier data is pivotal for ensuring accurate information, mitigating ongoing supplier-related risks, and avoiding supply chain disruptions.
And through big data tools, you can easily achieve that.
To recap, procurement professionals can leverage big data not only to find the best suppliers but also to continuously monitor, analyze, and manage their performance metrics and compliance.
This, in turn, contributes to enhanced cost management and strengthened supplier relationships for the company.
In demand forecasting, big data plays a pivotal role in enhancing the accuracy of demand predictions and optimizing inventory management.
By analyzing vast datasets encompassing historical sales, market trends, and external factors, organizations gain insights into customer behavior and demand patterns, enabling them to align sourcing strategies with current customer demand.
For example, Amazon uses machine-learning algorithms to analyze product purchasing data and make data-driven demand forecasts that help the company optimize inventory levels and ensure customer satisfaction.
You can learn more about this process in the Forbes article shown below.

Source: Forbes
Since advanced algorithms and machine learning models process demand-related data in real time, this allows for more precise predictions and proactive adjustments to inventory levels.
This not only minimizes the risk of stockouts or overstock situations but also enables companies to communicate forecasted shifts in demand to their suppliers, allowing them to adjust and thus strengthening supplier relationships.
All in all, big data and demand forecasting are a perfect fit, enabling companies to increase the precision of their forecasts, align their inventory with market demand, enhance supplier collaboration, and reduce risks associated with suppliers and markets.
Having covered how big data can be used in procurement, let’s turn to key technologies that are needed and typically utilized for obtaining, processing, and analyzing big data—machine learning, cloud computing, and data analytics.
Machine learning (ML) is a subset of artificial intelligence (AI) that equips software systems with the ability to learn and improve from experience without being explicitly programmed.
The machine learning process involves creating algorithms designed for specific purposes and using initial data to train the model, enabling it to produce the desired results.

Source: Veridion
The most impressive thing about these models is that they continue to learn and improve over time, thereby enhancing their performance and results.
As we mentioned, ML models are used in various procurement scenarios to analyze vast datasets and identify patterns, trends, and anomalies, facilitating tasks like strategic sourcing, spend analysis, supplier relationship management, and demand forecasting.
In the context of big data in procurement, cloud computing is an indispensable element. Big data could hardly be managed if we would depend on old-school, on-premise software.
Luckily, cloud-based applications are a common thing nowadays. Cloud computing provides scalable and on-demand access to a range of services, tools, and applications over the Internet.
Here’s how Investopedia defines it:

Source: Investopedia
This definition implies that, for instance, large datasets can be processed and accessed without the need for extensive on-premises infrastructure.
Today, procurement teams can utilize a range of flexible and affordable cloud-based applications to seamlessly integrate big data analytics into their procurement processes.
Data analytics is where the powers of big data, machine learning, and cloud computing converge to process and interpret vast datasets, extracting valuable insights, patterns, and trends that enhance decision-making in procurement processes.
Data analytics tools can take various forms, ranging from standalone software systems to easily integrated solutions like APIs, providing flexibility and adaptability for different procurement needs.
Procurement analytics platform from Datapine
In summary, these key technologies—machine learning, cloud computing, and data analytics—form the backbone of big data applications in procurement, offering advanced capabilities to analyze, interpret, and derive actionable insights from large and complex datasets.
To maximize the benefits of big data in procurement, companies need a strategic approach to incorporating it into their processes. So let’s explore that.
Clearly defining objectives is the first step in harnessing big data’s power.
In other words, you first need to determine which goals you’re trying to achieve and what kind of data is most relevant for achieving them.
This starts with identifying general procurement goals, such as those in the example below.
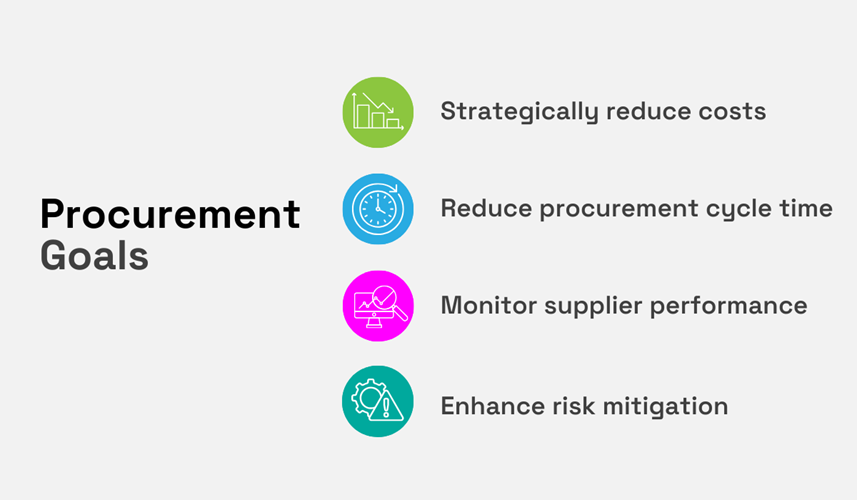
Source: Veridion
From there, move to determine more specific objectives, such as improving supplier discovery, enhancing spend analysis, or streamlining demand forecasting.
Naturally, these objectives should be SMART (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound).
They will serve as guiding principles, ensuring that big data initiatives align with overarching procurement strategies.
When selecting big data solutions, evaluate your current procurement technologies and assess their compatibility with such tools.
Why?
Because integrating big data solutions with legacy procurement systems can pose challenges due to differences in data formats, structures, and technology standards.
You want to ensure that any big data tools you opt for can seamlessly connect to your existing systems, enabling a real-time data flow and comprehensive analyses without the need for manual syncs and updates.
To enable smooth integration, big data providers typically provide integrations with other popular procurement-related tools.
Sometimes software uses third-party data and integrates it into their system and sometimes integration of two tools is done via API.
For example, Sievo has both data partners and technology partners, which means that data from these partners integrates within the Sievo software.

Source: Sievo
Overall, you will have better use of big data if you can integrate it properly with other tools you use for optimizing your procurement processes.
Cross-departmental collaboration and information sharing are essential prerequisites for the successful implementation of big data in procurement.
Even without big data, close collaboration between departments such as procurement, IT, finance, operations, and production proves invaluable for discovering cost-saving opportunities, ensuring accurate demand planning, and identifying areas for improvement.
The three Cs of teamwork—collaboration, communication, and coordination—constitute the foundation of successful companies boasting high-performing, cross-functional procurement teams.
When such procurement teams are enhanced by big data, they gain a data-driven edge.
This empowerment allows them to excel in cost-saving, demand planning, and process improvement, driven by strategic insights and more informed decision-making.
Therefore, the synergy of big data capabilities with open communication and collaboration across departments ensures a holistic understanding of procurement data needs, facilitates a more unified approach, and generates superior results.
It’s safe to say that, moving forward, big data tools and analytics will become an integral part of modern procurement processes.
Big data has the potential to transform many facets of the procurement process, leading to quicker and easier supplier sourcing, more comprehensive spend analysis, enhanced supplier management, and more accurate demand forecasts.
Therefore, we hope this guide inspires you to explore and implement big data solutions in your procurement strategies, leveraging the transformative power of data-driven insights for more efficient, cost-effective, and strategic procurement practices.