Challenges of Using Big Data for Procurement

In the world of large-scale procurement, the potential benefits of leveraging big data tools are immense, promising cost-savings, maximized value, minimized risks, and enhanced efficiency of the entire procurement process.
Naturally, these big opportunities come with some specific challenges.
Procurement departments grapple with issues like overwhelming data volumes, poor data reliability, data fragmentation, or resistance to new technology, and need tools and methods to address them.
Today we’ll explore these challenges and provide insights into effective solutions for utilizing big data to achieve a more streamlined, data-driven procurement future.
Having to deal with copious and ever-growing amounts of data from various sources can be a challenging task for procurement teams.
For starters, consider the sheer volume of internal data integral to procurement processes, such as the data:
Now add to that external data sources, such as public systems containing information on suppliers, commodity prices, and market trends, and proprietary business intelligence systems offering additional information like supplier industry codes, risk profiles, and credit ratings.
Lastly, also consider external big data databases and their role in enhancing supplier discovery.
To better illustrate this intricate web of internal and external datasets, here’s an overview:
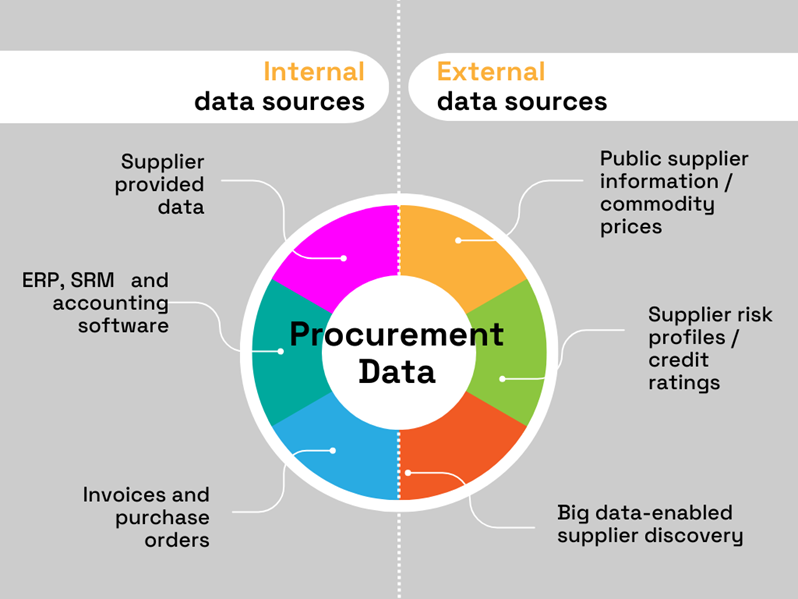
Source: Veridion
Given the mere volume of data used in procurement and the speed at which more data is generated, it’s no wonder that procurement departments often find themselves drowning in an ocean of data.
And why is that the problem?
Because rapidly growing datasets increase the likelihood of encountering redundant, duplicate, or outdated information, making it challenging to assess what is relevant and extract meaningful insights.
For instance, too much data can make the process of finding and vetting new suppliers too long, forcing the company to cut corners and choose from a limited pool of existing suppliers without thoroughly evaluating their suitability, capabilities, or past performance.
Such rushed decisions can lead to suboptimal choices, increased risks, and potential disruptions in the supply chain.
To overcome this challenge, procurement professionals can leverage data management systems and analytics tools that can turn big data into actionable insights.
For example, data analytics tools (alone or as part of an application suite) use large internal and external databases to extract complex procurement insights, enabling stakeholders to understand trends and make informed decisions.
When such tools are big data-enabled, they can significantly enhance this process by integrating and organizing internal datasets and enriching them with real-time data from external sources.
Their data storage, processing, and analytic capacities far exceed the capabilities of traditional software systems by employing two key technologies: machine learning and cloud computing.
Machine learning (ML) and deep learning neural networks are a subset of artificial intelligence (AI) used to create algorithms and models that empower advanced analytics tools in procurement to learn from historical data, recognize patterns, and reach accurate conclusions.

Source: SCS
As for cloud computing, cloud data storage solutions provide flexible and affordable infrastructure that eliminates the need for extensive on-premises data storage.
At the same time, when cloud-based tools are powered by AI and machine learning, they can save procurement teams a lot of time and effort invested in data processing, categorization, refinement, and analysis, allowing them to efficiently handle vast datasets.
And procurement teams across the globe have started leveraging these technologies.
Hackett Group’s 2022 study showed that, in the procurement arena, legacy systems are being quickly replaced by cloud-based procurement application suites while a growing number of companies are adopting advanced analytics solutions.

Illustration: Veridion / Data: Hackett Group
These technologies, when capacitated to handle large and diverse datasets, can be considered components of the broader big data ecosystem.
Overall, the challenge of managing the volume of internal and external procurement data can be effectively addressed by using big data tools to automate manual processes and enable data-driven decision-making.
Big data introduces several complexities that can impact the accuracy and dependability of the data.
For example, one common issue is data inaccuracies stemming from manual input errors or outdated information.
The complexity of big data analytics tools and the interpretation of results can introduce the potential for human error.
Similarly, when procurement teams rely on out-of-date supplier databases, they may encounter discrepancies in supplier details, leading to incorrect evaluations.
Another reliability concern is incomplete data.
Big data often involves integrating data from various sources, and the reliability of this data can decrease due to inconsistent formats or missing values.
That leads to gaps in information and affects the reliability of data analysis.
Poor data seems to be very common.
According to Rosslyn’s white paper, the estimated cost for US companies due to inaccurate or missing data (also known as bad/dirty data) exceeds $600 billion a year.
At the same time, less than 50% of company managers are confident about the reliability of their data.

Illustration: Veridion / Data: Rosslyn
The reasons behind so low confidence in data reliability and such high losses primarily stem from:
As you can see, unreliable data may stem from various sources. Regardless of its source, bad data hinders the procurement team’s ability to make well-informed decisions.
Such data is an obstacle to finding relevant suppliers, comparing them to identify the best ones, negotiating beneficial contracts, assessing the risk of working with those suppliers, etc.
To address these challenges and enhance the reliability of big data in procurement, organizations need to implement robust data governance practices, invest in data quality management tools, establish clear data standards, and ensure continuous monitoring and validation of data sources.
Regular audits and validation checks are essential to identify and rectify data discrepancies, ensuring that procurement decisions are based on reliable and accurate information.
And when it comes to accurate information, that’s something we at Veridion are very proud of.
With Veridion, you get access to a global, weekly updated, supplier database with over 80 million company entries covering 300 million products and services.
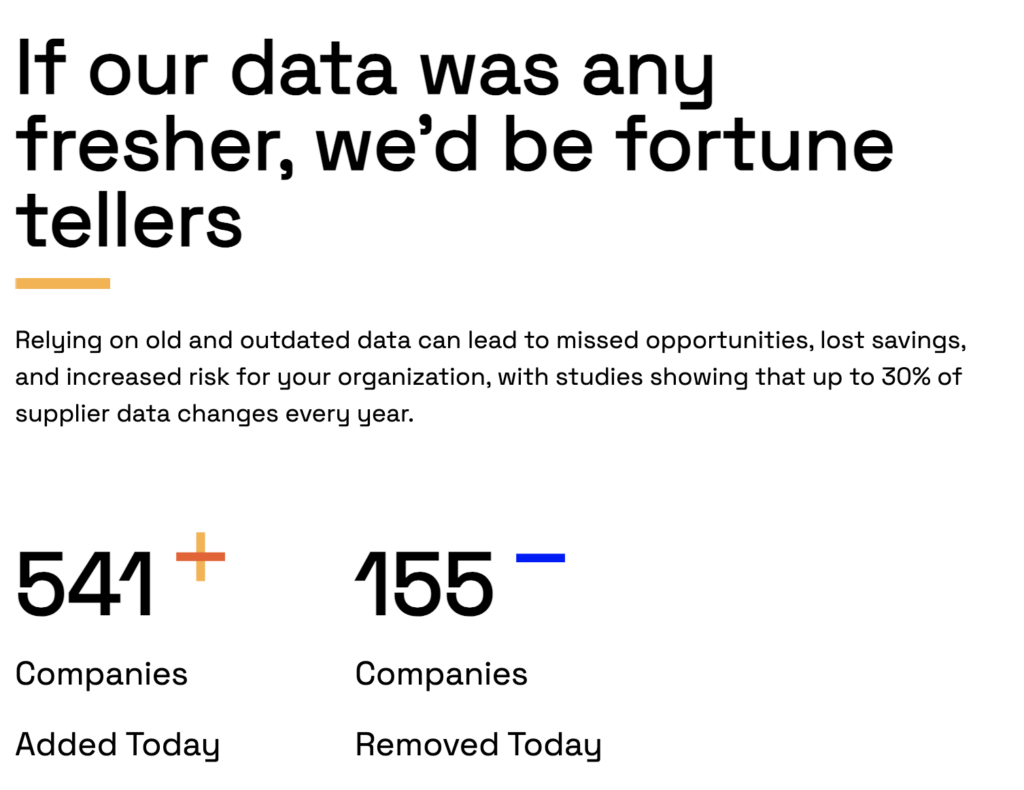
Source: Veridion
All of that happens through a Search API that integrates the data to run with your other software systems.
This not only accelerates supplier discovery and sourcing but also ensures that the supplier data is always current, thus eliminating data reliability concerns.
Furthermore, you can use Veridion’s AI-powered Match & Enrich API to organize, de-duplicate, and ensure real-time updates of your supplier records.
In conclusion, ensuring data reliability in procurement is pivotal for making accurate decisions, so make sure you standardize your data formats and harmonize different types of data to have reliable insights.
Data fragmentation in the context of big data refers to the division or distribution of data across various sources or systems, making it challenging to integrate and analyze cohesively.
Procurement relies on a comprehensive understanding of various factors such as supplier performance, market trends, and internal demand.
But when relevant data is fragmented across different systems or departments, procurement teams may lack complete visibility.
This incomplete view hinders their ability to make well-informed decisions.
Not to mention that fragmented data often comes with inconsistencies in terms of format, and structure.
Just sheer differences in naming conventions or measurement units can cause data quality issues and result in unreliable analyses.
The issue of data fragmentation and complexity spans wide.
In fact, it’s the top challenge for companies undergoing digital transformation, as revealed by a 2021 study of chief data officers (CDOs).
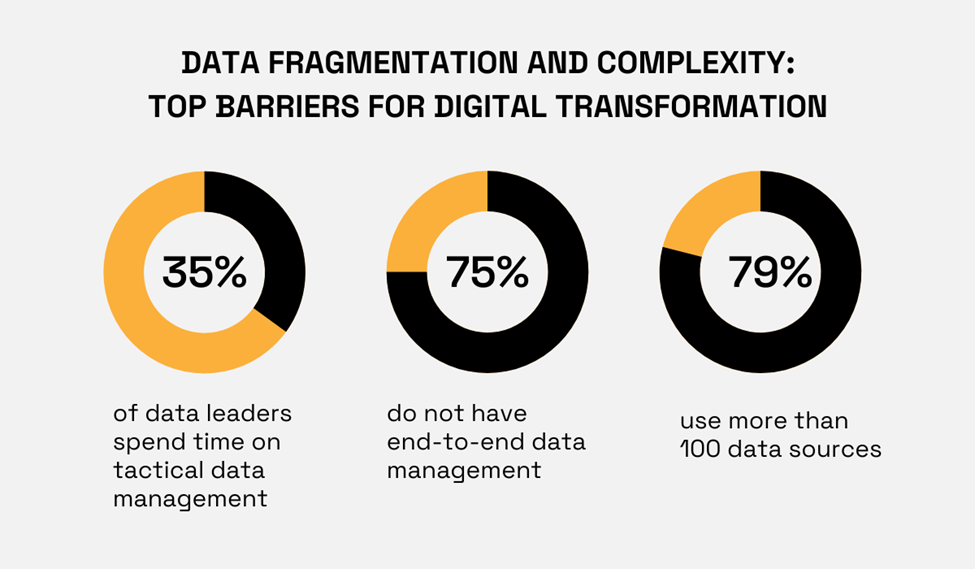
Illustration: Veridion / Data: Informatica
Depending on the level of data fragmentation and the number of data sources, it’s no wonder that many organizations don’t have a unified view of data and therefore struggle to gain comprehensive insights.
So, how can organizations and their procurement departments address these issues of fragmented information?
Simply put, they should invest in technologies and strategies that enable effective data integration, standardization, and governance.
Focusing on data standardization and consolidation of data into a single platform is a good place to start.
This can be achieved with the help of master data management (MDM) systems that take a company’s critical business data on customers, products, assets, and suppliers and consolidate it into one unified dataset. A single source of truth.

Source: DSA
The establishment of a unified, regularly updated version of master data that can be shared across various business units and IT systems ensures that all stakeholders have access to the same data.
Moreover, the process that precedes the inclusion of data into the master database, such as data cleansing, reformatting, consolidation, and standardization, addresses issues like data duplication, inconsistency, and inaccuracy.
Dealing with fragmented data requires significant resources, both in terms of time and technology.
Procurement teams may need to invest in data integration tools, data cleansing processes, and expertise to manage and make sense of data scattered across different systems.
Despite the transformative potential of big data in procurement, organizations often encounter resistance from employees unaccustomed to new tools and processes.
If they don’t feel comfortable using big data tools or lack the technical expertise, they might struggle to effectively collect, analyze, and interpret the vast amount of data that is suddenly available.
To address this challenge, companies should employ a twofold approach.
First, they should ensure that the significance and benefits of integrating big data into procurement processes are clearly communicated to relevant employees.
Concurrently, they should invest in comprehensive training programs to provide employees with the necessary skills and knowledge to efficiently harness the power of big data tools.
Naturally, such programs can be designed internally with the help of big data technology providers or outsourced to external organizations. Below is one example of such training.

Source: Purchasing & Procurement Center
These training initiatives should empower relevant procurement staff on how to utilize big data tools in data collection, analysis, and interpretation.
Moreover, companies should gradually implement big data initiatives to allow employees to adapt slowly.
Overall, a phased roll-out of big data tools, as well as proper employee awareness-raising measures and training programs can help companies mitigate resistance to big data technologies and methods.
Ultimately, the goal is to foster a data-driven culture where the workforce is not only comfortable with big data tools but also sees them as invaluable assets in optimizing procurement outcomes.
Big data in procurement is here to stay.
To get the most out of big data capabilities, you have to carefully manage the challenges we covered, to ensure the reliability of your data analyses.
When these challenges are properly addressed, the benefits of leveraging big data exceed any time and effort invested in big data, bringing improved efficiency, minimized risks, lower costs, and higher profitability to your company.