4 Best Practices for Managing Your Supplier Database


Key Takeaways:
Managing your supplier database might not sound exciting, but it’s the backbone of effective procurement.
Inconsistent records, outdated profiles, missing information, and security gaps don’t just create headaches—they lead to higher risks, costly mistakes, and missed opportunities.
The good news?
With the right approach, supplier data can become a powerful asset, helping your procurement team make smarter, more informed decisions.
How?
By applying the best practices explored in this article.
Standardizing supplier data entry is the foundation of a well-structured database.
Without clear procedures and rules for how data is recorded, inconsistencies creep in—supplier names are entered differently, key details are omitted, and duplicate records pile up.
Moreover, different departments use siloed systems with their own data classifications and entry conventions, making inter-system data legibility difficult.
Ultimately, these issues make it harder to track spending, assess supplier performance, and ensure compliance.
Unfortunately, this is a widespread problem.
A recent TealBook survey found that 53% of procurement professionals rate their supplier data as poor.
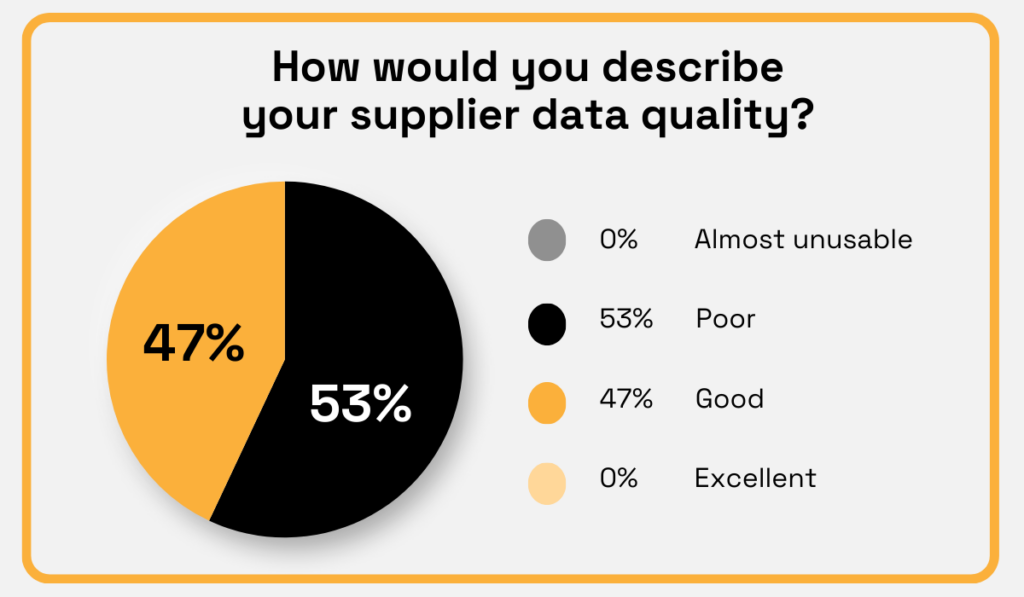
Illustration: Veridion / Data: TealBook
As shown, none of the respondents consider their supplier data unusable, but none rated it excellent either.
For companies aiming to improve data quality, the first step is standardizing data entry.
So, let’s look at some best practices that can ensure data consistency and accuracy.
One of the biggest sources of inconsistent supplier data is naming variations.
A single supplier might appear under different spellings, abbreviations, or formats across departments and systems, leading to errors in reporting and analysis.
To prevent this, companies should implement standardized naming conventions, ensuring uniform abbreviations and formats across their systems.
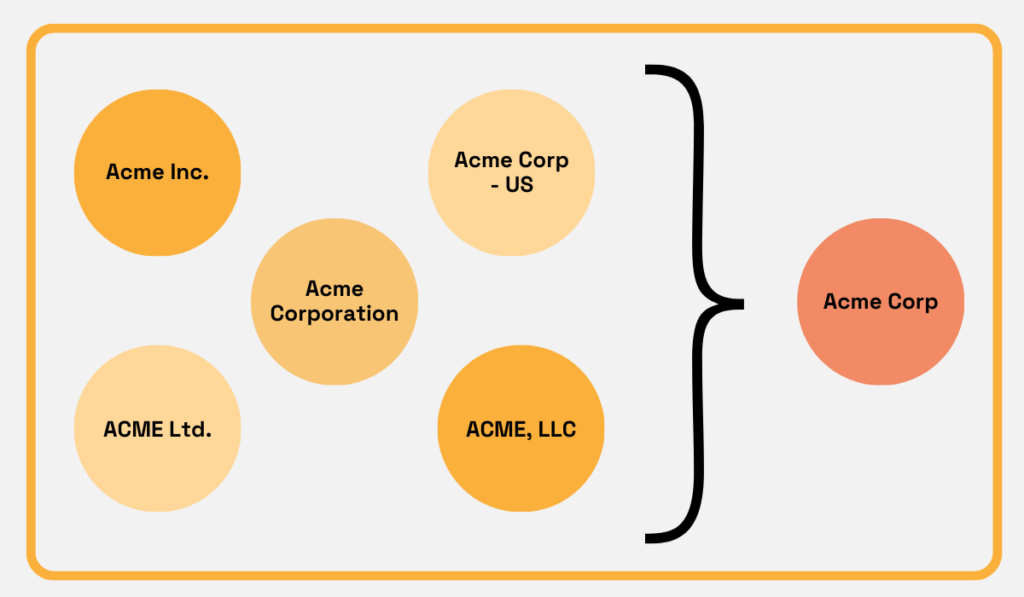
Source: Veridion
This standardization should also extend to other key supplier data elements, such as ISO country codes and address formats.
Next, organizations should define the required data fields for supplier records, such as company name, ID number, and industry classification.
Moreover, they should ensure identical field names across all systems.
Additionally, procurement systems should integrate data validation rules and templates to prevent manual entry errors.
These can include required fields (marked with asterisks), error messages for incorrect entries, and dropdown menus enforcing standardized options, such as the one shown here.
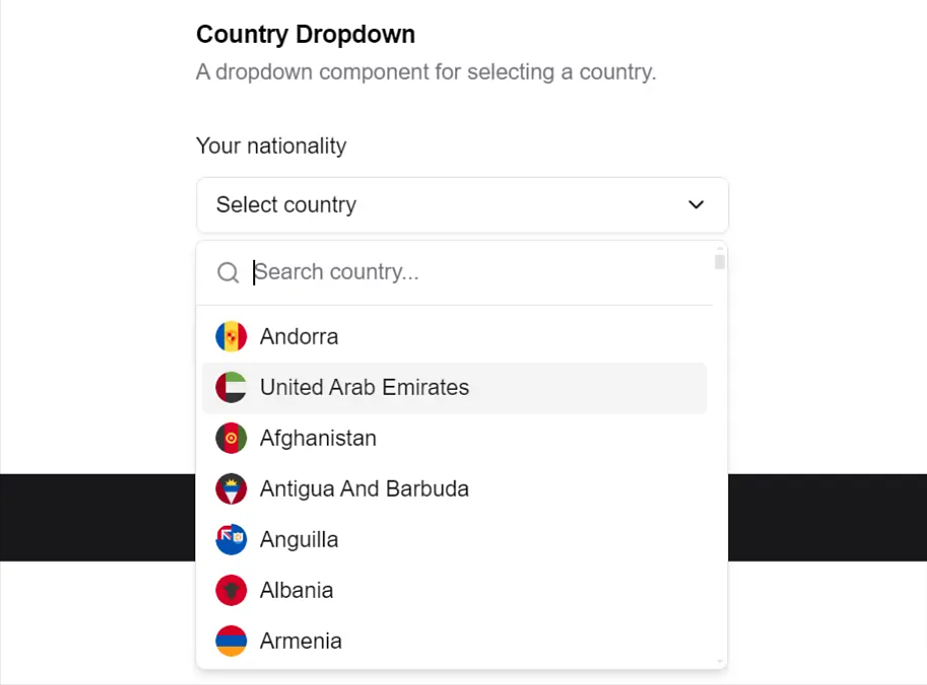
Source: NextGen JavaScript
On the human side, training employees on standardized data entry further improves accuracy and reduces inconsistencies.
Beyond standardized data entry, it’s important to keep the ultimate goal in focus—creating a centralized, integrated supplier database—a single source of truth for all company users.
Implementing a master data management tool designed to consolidate and synchronize supplier data across systems is often the most effective approach.
Here’s an example of one such tool, HICX.

Source: HICX
As shown, this tool enables you to consolidate supplier data from various ERP, P2P, and other systems into a single, unified master database.
To recap, data entry standardization sustains consistency by enforcing naming conventions, required fields, and validation rules across all systems.
The goal is to ensure every new entry follows a unified structure, keeping supplier records accurate, reliable, and easily searchable.
A supplier profile is more than just a company’s name and contact details—it’s a structured record containing key information about the supplier.
Optimizing supplier profiles in your database makes life easier for procurement teams, improving efficiency and enhancing decision-making.
More specifically, well-structured and regularly updated supplier profiles enable them to:
But what should a supplier profile include?
Ultimately, this depends on which supplier data is most relevant for your organization.
If you’re using procurement software, some profile elements are predefined, while others can be customized.
To illustrate, here’s a supplier profile dashboard in SAP Ariba Strategic Sourcing Solution:
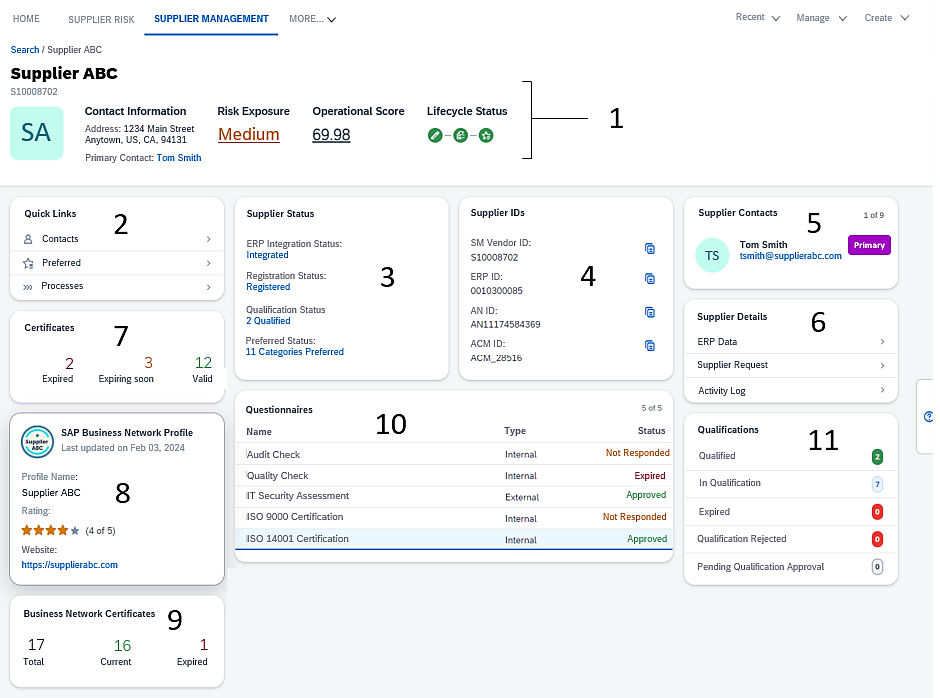
Source: SAP
As shown, this profile covers all the key supplier details, from contact information and risk exposure to operational score and lifecycle status.
It also serves as a good example to discuss specific data fields that could be included in your optimized supplier profiles.
For instance, including key performance metrics such as capacity levels, delivery times, and quality ratings helps assess supplier reliability and predict future performance.
Likewise, insights into important compliance data, such as ISO certifications, questionnaires, audit results, and quality checks, help ensure suppliers meet regulatory and quality standards.
Of course, supplier risk exposure is a must-have element.
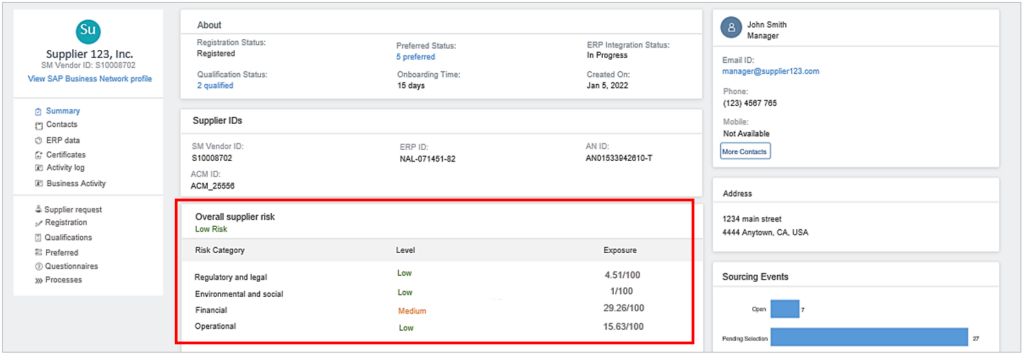
Source: SAP
A clear and regularly updated risk profile assists teams in making informed sourcing decisions based on real-time data.
Another key component is contract details, pricing, and payment conditions.
Having an overview of contract-specific clauses, contract history, past compliance, and agreed payment terms aids in decision-making and negotiating better terms going forward.
It also allows teams to track contractual obligations and manage supplier relationships more effectively.
Beyond individual data fields, optimizing supplier categorization is essential.
In a nutshell, supplier categorization allows your procurement team to easily search and filter suppliers in the database based on specific criteria.
This further streamlines the sourcing process and enhances decision-making.
To illustrate this, here’s a typical tier-based approach many companies use:
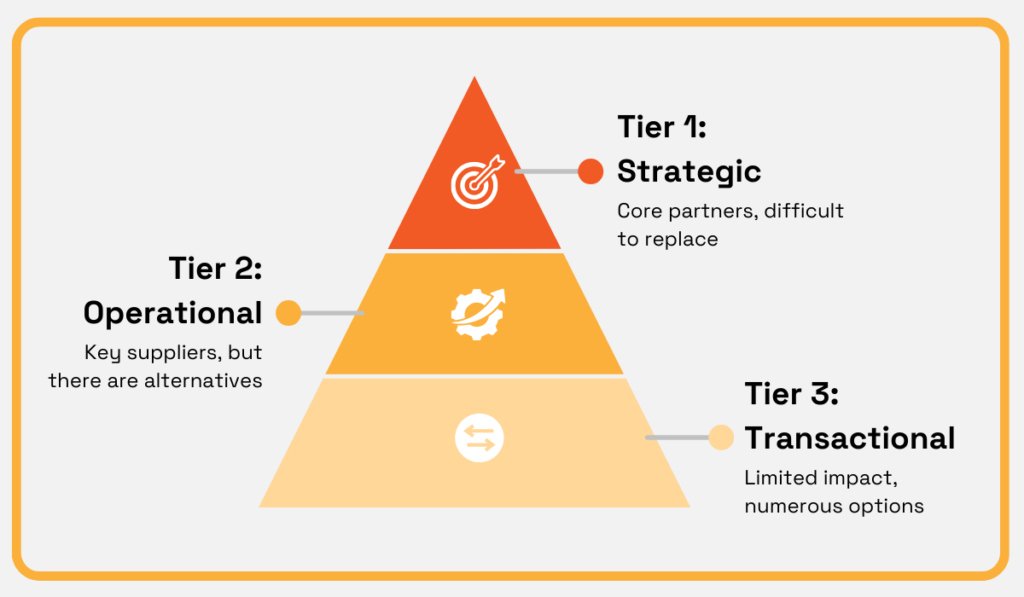
Source: Veridion
As shown, the tier-based categorization provides a straightforward way to classify suppliers based on their importance to your business.
When these classifications are available in supplier profiles, procurement teams can more effectively prioritize suppliers, allocate resources, and tailor sourcing strategies.
All the data fields and supplier information elements we’ve covered allow your team to segment suppliers based on performance, risk levels, and strategic importance.
As mentioned earlier, supplier profiles should be centralized within a single database, accessible to all company users with proper access permissions.
Finally, to enable effective, real-time decision-making, it’s crucial to ensure that supplier profiles are dynamically updated to maintain data accuracy—our next best practice.
Manually maintaining supplier data is both time-consuming and prone to human error.
Procurement teams often struggle with outdated records, missing information, and inconsistent formatting, all of which create inefficiencies.
Worse, incorrect supplier data—such as expired certifications or inaccurate tax IDs—can lead to financial losses, compliance violations, and supply chain disruptions.
Many organizations fail to recognize these risks until they result in costly mistakes.
Omera Khan, professor of supply chain management at the University of London, says that many companies still don’t fully realize the costs of incomplete, outdated, or low-quality supplier data.
She further explains:

Illustration: Veridion / Quote: HICX
When addressing these challenges, companies can turn to automation to ensure supplier data accuracy.
Automated solutions minimize manual data entry and standardize information, reducing the risk of human error.
Additionally, various automation tools help verify supplier credentials, tax IDs, and business registrations while maintaining accurate tax and banking details.
Take, for instance, Esker’s automated supplier management solution.
Among its many capabilities, it automatically verifies supplier bank account details, eliminating manual errors and reducing the risk of fraud.
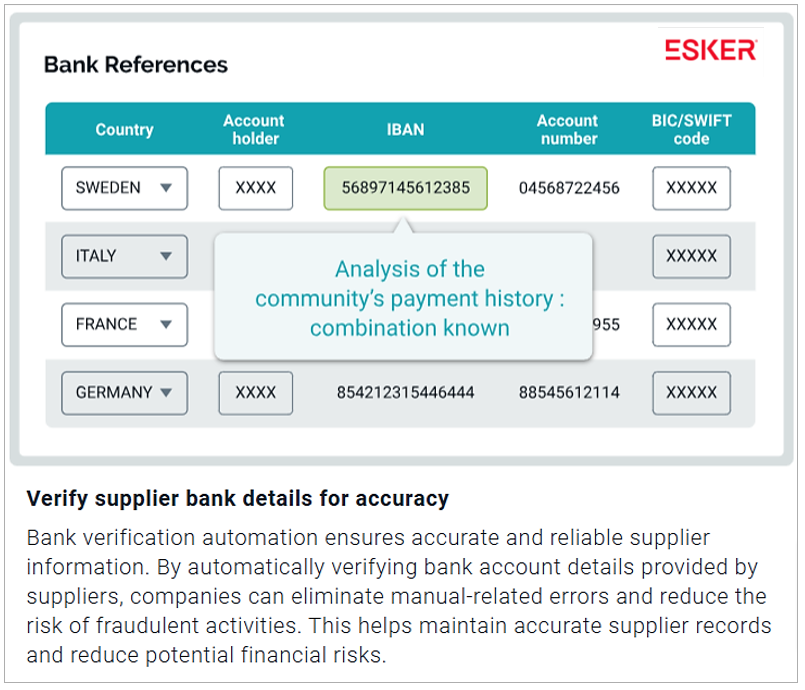
Source: Esker
Another key area ripe for automation is supplier details that frequently change and require regular updates.
Supplier self-service portals can help by allowing suppliers to update certifications, banking details, and compliance documents directly.
However, while useful for certain aspects of supplier management, self-service portals do not provide real-time insights into a broader range of critical data points.
For example, suppliers may be reluctant to report financial instability, unethical practices, or regulatory non-compliance.
Likewise, they might not disclose—or even be aware of—external factors affecting their risk profile, such as shifting market conditions, geopolitical events, or new regulations.
This is where AI-driven supplier data enrichment comes in.
As Rahul Asthana, a supply chain management expert, highlights:

Illustration: Veridion / Quote: GainFront
These AI-driven solutions continuously scan vast amounts of external data, verify its authenticity, classify relevant information, and convert it into real-time insights on suppliers.
This level of automation reduces reliance on suppliers to self-report critical updates, ensuring sourcing decisions are based on the most accurate and comprehensive information available.
One such AI-powered supplier data enrichment service is our Veridion.
If you’re interested in how supplier profile enrichment works in Veridion, watch this short video:
Source: Veridion on YouTube
With just the name and address of a supplier, Veridion generates a fully enriched profile in seconds.
Another key advantage is its ability to deliver automated real-time alerts on specific risk factors.

Source: Veridion
As shown, Veridion allows you to set custom risk factors, and when AI-driven monitoring detects relevant events, you receive real-time alerts with data confidence scores.
By integrating real-time data feeds, procurement teams can detect early warning signs—such as financial instability, regulatory issues, or supply disruptions—before they escalate into major risks.
Beyond ensuring data accuracy, automation transforms supplier data management from a reactive, manual process into a proactive, data-driven strategy.
Ultimately, this enhances procurement efficiency, mitigates supplier risks, and enables smarter sourcing decisions.
Strong data security is crucial to avoid costly breaches that can lead to operational disruptions, reputational damage, and regulatory fines.
One common risk is weak access control, which can allow unauthorized employees to access sensitive supplier records, either intentionally or unintentionally.
Even viewing supplier information can lead to the exploitation of details for malicious purposes, like fraud or procurement rigging.
Moreover, unauthorized changes to data can ultimately compromise critical processes such as spend analysis, supplier evaluations, and decision-making.
To mitigate these risks, role-based access control (RBAC) is now a standard feature in many procurement software solutions.
Here’s how RBAC works:
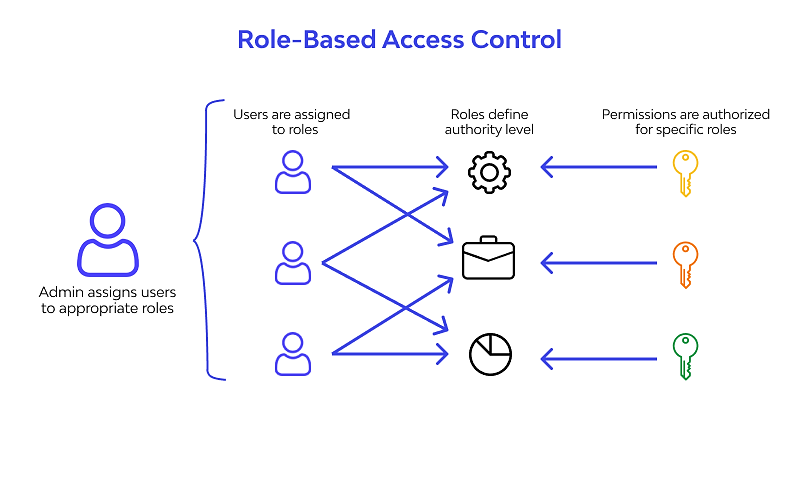
Source: Wallarm
In practice, this means that specific roles are assigned to users based on their job responsibilities.
These roles define the level of access each user has, ensuring that only authorized personnel can view or modify sensitive supplier data.
Beyond RBAC, most software tools also provide access logs and audit trails, which can be monitored to track data modifications and detect anomalies.
Another growing security risk is cyberattacks, which can expose confidential information and even disrupt entire operations.
That’s what happened to Toyota in 2022 when it had to halt production across all its Japan-based plants.
The cause?
A cyberattack on the systems of Kojima, a key supplier of plastic automotive parts.

Source: Security Magazine
Since Toyota’s systems relied on communication with Kojima’s, the disruption forced a temporary shutdown.
This example highlights that data security isn’t just about internal controls—it also depends on the suppliers’ cybersecurity measures.
A single weak link, whether within your own systems or a supplier’s, can lead to major disruptions.
To mitigate these risks, you should not only use encryption protocols to protect sensitive supplier data but also assess and verify the security measures of your suppliers.
One essential safeguard is enforcing multi-factor authentication (MFA) for logins into your systems, including the supplier portal.
As shown below, MFA is a standard security feature in leading procurement solutions like SAP Ariba, Jaggaer, or Coupa.
Source: Coupa
Another key practice for maintaining strong supplier data security is regularly reviewing user permissions.
This applies to both internal employees and external suppliers, ensuring that only authorized individuals can access critical data.
Additionally, conducting regular security audits helps identify vulnerabilities, reinforce internal controls, and ensure compliance with data protection regulations.
To sum up, strengthening the security of systems that feed into your integrated supplier database enhances data reliability, supports compliance, and reduces the risk of breaches.
These four best practices are essential for maintaining a well-managed supplier database, ensuring that the information remains reliable and up-to-date.
By standardizing data entry, creating consistent supplier profiles, and utilizing automation for improved accuracy and security, organizations can turn fragmented supplier data into a powerful strategic asset.
Additionally, integrating supplier-related systems and standardizing data exchanges further strengthens the value of the database, making it a key resource for smarter procurement decisions.
Hopefully, you will adopt these best practices and optimize your supplier data management.