How to Develop an Effective Supplier Database


Key Takeaways:
Procurement leaders see poor supplier data as one of the main obstacles to digital transformation and efficient processes.
Luckily, there are a few simple steps you can take to rapidly improve data quality.
By developing an effective supplier database, small, mid-, and enterprise-level businesses can unlock valuable supplier management insights and build competitive advantage.
Curious about the process and how it can benefit your organization?
Let’s dive right in.
Effective supplier databases are designed based on clear objectives.
No goals means no strategy, and without a strategy in place, you won’t get the desired results even if you invest a lot of time and resources into this process.
To avoid that, let’s first take a step back and establish what a supplier database is.
The main function of such a database is to centralize supplier data and facilitate its effective tracking and management.

Source: Veridion
Creating an effective database can help solve data fragmentation issues, but it can also lead to new problems if not managed properly.
For instance, if you were to include absolutely all supplier information, navigating your database would become very difficult and time-consuming.
Conversely, clearly defining your supplier database goals helps you determine which information to include based on your organization’s specific needs and goals.
Some of the most common ones include enhancing supplier visibility and compliance, or optimizing costs, for example.
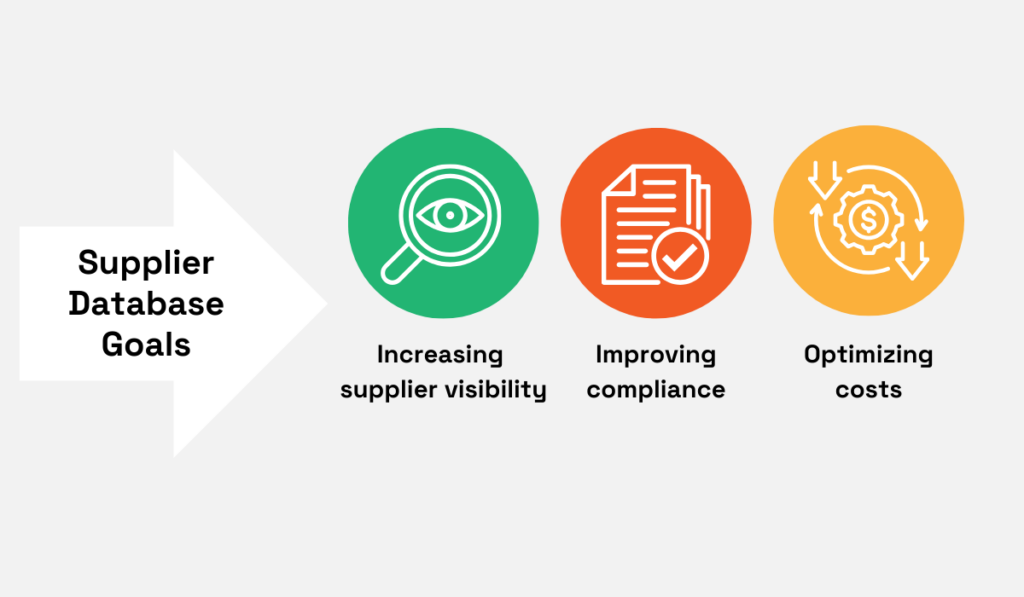
Source: Veridion
This sets the foundation for an effective data collection process.
So, how do you decide which data to collect?
For starters, consider the three types of data that serve specific purposes.
| Business profile data | Basic supplier information, from contact and product/service details to references, certifications, and contract terms. |
| Performance data | Delivery reliability, product and service quality, contract compliance, progress tracking, and customer satisfaction metrics. |
| Risk management data | Supplier’s financial situation and various risk factors, including ESG compliance, geopolitical risks, supply chain vulnerabilities, and overall operational stability. |
Let’s say you want to increase supplier visibility.
In that case, your database should foreground supplier status and performance trends.
Besides up-to-date business information, a comprehensive overview of total spend and performance data would support efficient supplier segmentation.
Meanwhile, focusing on risk management data would mean combining performance tracking with real-time monitoring of labor, environmental, and financial risks.
As such, the database would be less focused on basic business data and integrate mechanisms to capture fresh data.
All in all, establishing clear objectives sets the stage for identifying the core data you want to collect, as well as the process and tools behind it.
Prioritizing specific supplier data points facilitates database navigation and better decision-making.
As we’ve established previously, businesses should have a clear overview of the supplier’s:
Structuring this information to ensure data accuracy and maximize business value is the most important part, though.
Research shows that, when done right, the process yields several benefits related to high-quality data, such as increased agility and improved decision-making.
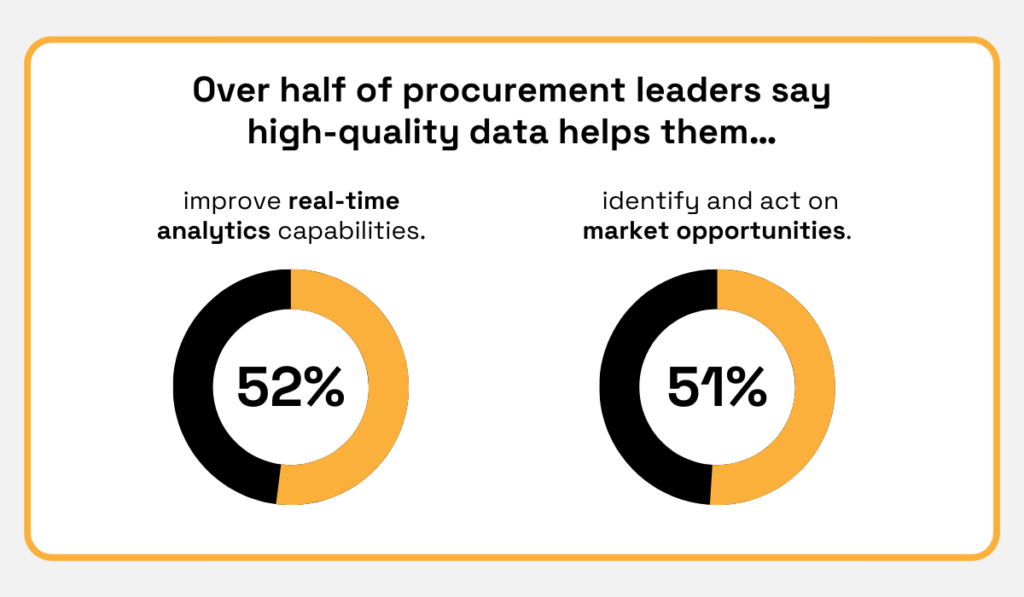
Illustration: Veridion / Data: TealBook
However, this is true only if the data is high-quality.
TealBook’s 2025 report shows that an alarming 53% of businesses rate their supplier data quality as poor.
Poor data quality costs organizations an average of $12.9 million a year, and while there are many reasons for this, one of the root causes is a lack of direction and strategy.
Among those warning about this trend is Myles Kleeger, former President and Chief Commercial Officer at Braze:

Illustration: Veridion / Quote: Forbes
Although Kleeger focused on customer data in particular, the same can be said for supplier data collection management.
So, what do you do to counter this?
Begin by narrowing down the type(s) of data you need to collect.
Only then can you determine which data collection processes and sources you should rely on.
An important thing to keep in mind is that the data type dictates the frequency of updates.
For example, supplier contact information or certifications can be checked and refreshed periodically, while performance metrics or risk assessments require more regular updates.
Your priority data points will also come from different sources.
Supplier data sources can be broadly divided into internal and external sources.
Then there’s also data collected through direct interaction, from self-assessment surveys to on-site audits.
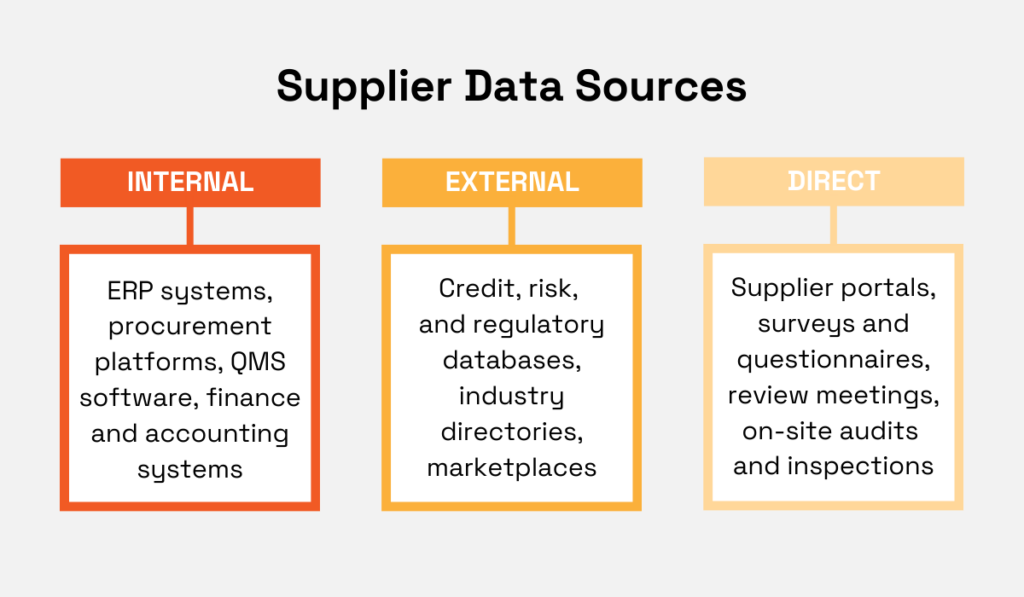
Source: Veridion
Thanks to the previous step, you can identify the most relevant sources more easily and ensure your supplier data is accurate, relevant, and reliable.
With all this in mind, it’s time to determine the kind of data management system you’ll be using.
Having a unified system for storing supplier data increases efficiency and effectively reduces discrepancies and errors.
Why?
Because trying to manage data across several systems increases the risk and frequency of errors.
This makes it all the more important to explore different options for managing supplier data, such as:
Excel spreadsheets are the most affordable option of the three while still enabling notable customization.
The minimal learning curve also contributes to its widespread use, with one survey revealing that 68% of decision-makers report heavy reliance on Excel for exchanging data.
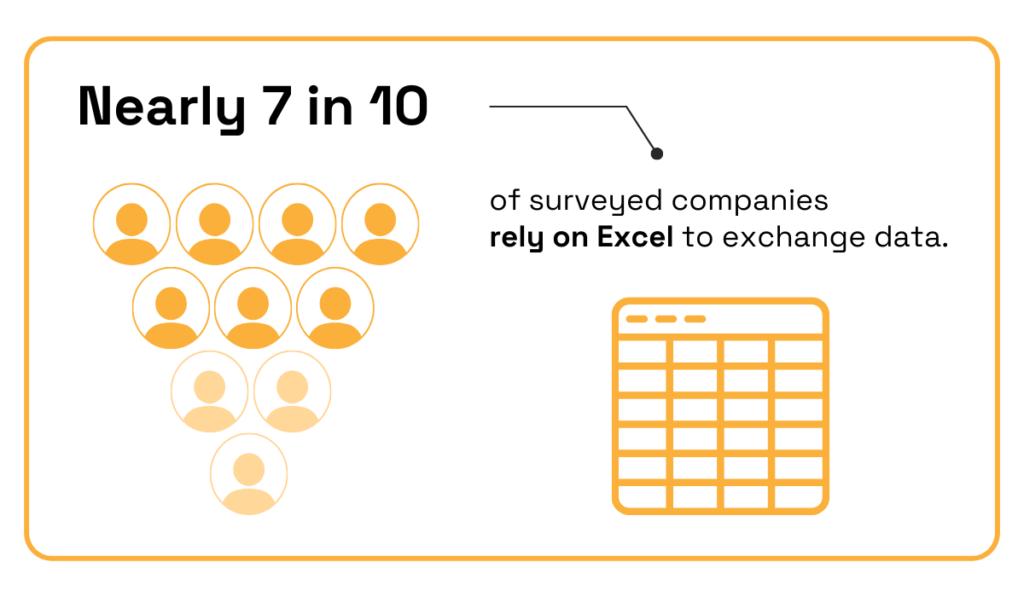
Illustration: Veridion / Data: XPLM
Although these figures seem like a strong vote of confidence in favor of spreadsheets, they actually reveal process inefficiencies causing information to slip between the cracks.
Namely, using spreadsheets makes it challenging to keep supplier data fresh even with a modest number of suppliers.
In fact, as you scale your business, it becomes downright impossible to do so.
Plus, you need to account for modern-day volatility.
Delivering results in the face of uncertainty requires larger supplier bases and sufficient agility, as noted by Malin Schmidt, Founder and Chief Executive at Kodiak Hub.

Illustration: Veridion / Quote: SiliconANGLE
Fortunately, different e-procurement tools will enable you to effectively manage supplier information even in the most dynamic landscapes.
These solutions are equipped with features that enable real-time updates and easy ERP integration, making them essential for companies with expansive supplier networks.
Cloud-based supplier relationship management (SRM) platforms like Kodiak Hub, for instance, also leverage AI-driven insights.
With over 250,000 actively managed suppliers and a focus on complex supply chains, Kodiak uses AI to produce detailed supplier profiles enriched from multiple sources, as shown below.
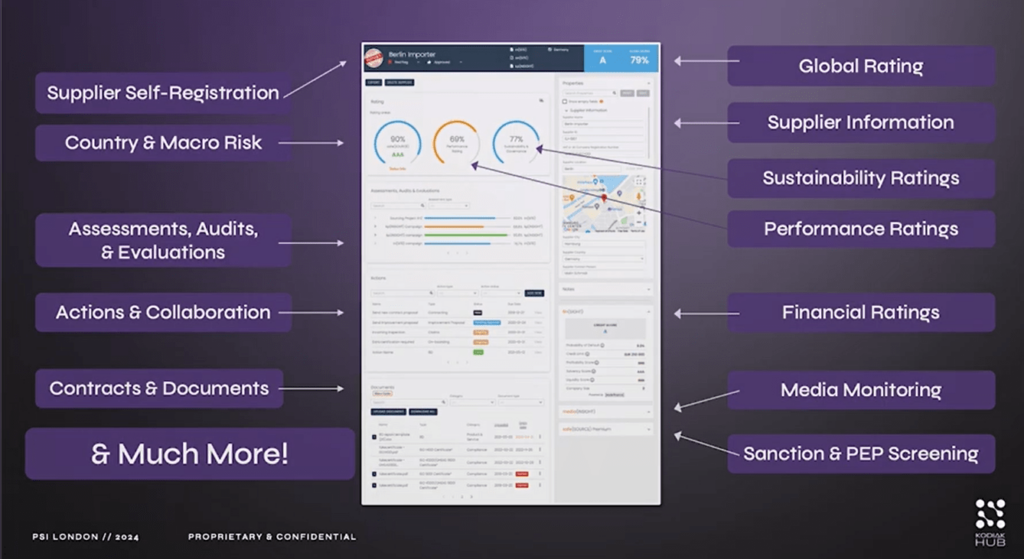
Source: Kodiak Hub on Youtube
The company claims these capabilities help reduce onboarding time by 80% and save about 10 work hours a week, while also improving supplier engagement by 90%.
More importantly, the ability to verify and validate key information by cross-checking multiple sources empowers users to make critical business decisions with confidence.
To sum up, while the advantages of modern solutions are clear, your best bet is to compare and contrast several options until you find the system that fits your circumstances.
Data management involves several stages.
With data standardization, you’re ensuring the consistency and usability of supplier information.
While the lack of data itself is an issue, misclassified or inconsistent supplier records can be equally as harmful.
Why?
Because it puts you at risk of missing consolidation and cost-saving opportunities, as well as leads to inefficient supplier evaluations.
In fact, poor data standardization is one of the biggest obstacles to effective digital procurement, as cited by the majority of CPOs.
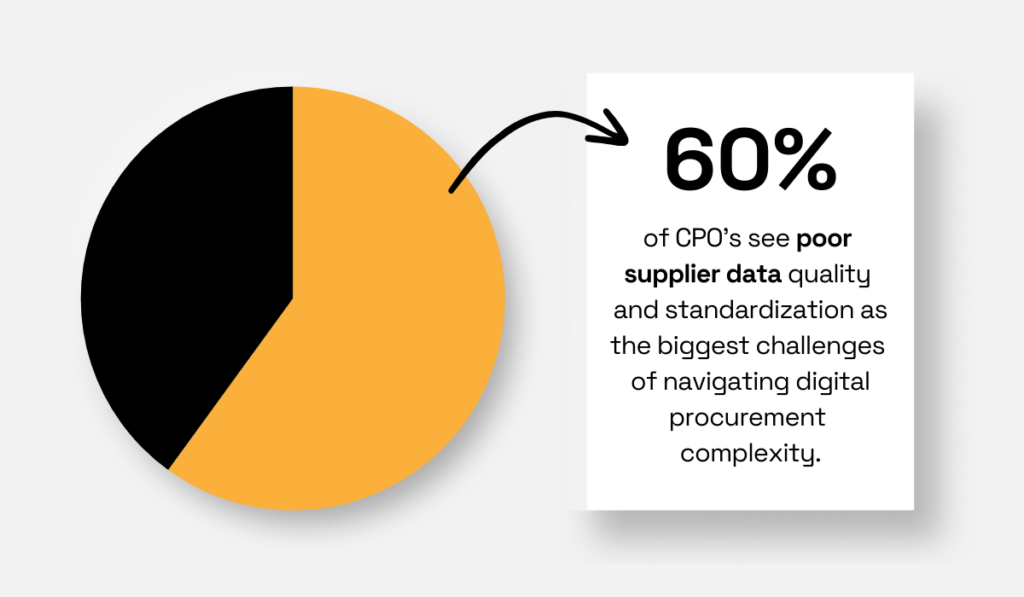
Illustration: Veridion / Data: HICX
And while procurement is inherently complex, data standardization doesn’t have to be.
What you can do to make things easier and mitigate these risks is to establish data collection guidelines that outline the format, structure, and units of measurement for the collected data.
In this way, you’re ensuring that the data from different suppliers and sources stays consistent, which in turn facilitates its integration into your existing systems.
Using standardized requests for information, proposals, or quotations typically creates the foundation for ongoing data management.
Here’s an example of one information request template that covers basic contact details and designated dates, and assigns a unique ID to each request.

Source: Smartsheet
Once you have the data, it’s important to categorize your suppliers to enhance visibility and risk management as well as streamline sourcing decisions.
These categories are typically defined based on:
Remember that you can save time by investing in automation.
Most software solutions provide list views that enable users to filter, sort, and analyze supplier data to get quick supplier insights from multiple angles.
Once you’re satisfied with the level of detail and data consistency, it’s time to take a closer look at relevant supplier performance metrics.
Measurable KPIs are the lifeblood of supplier database systems, enabling you to track individual supplier relationships and adjust your approach based on results.
Taking the time to define and track relevant supplier metrics, such as on-time delivery rates and quality consistency, does more than just capture supplier output.
It also ensures that both sides continue to derive value from the relationship in the face of business growth and changing priorities.
Yet, shockingly enough, KPMG’s research shows that over 40% of surveyed organizations have little to no insight into Tier 1 supplier performance.
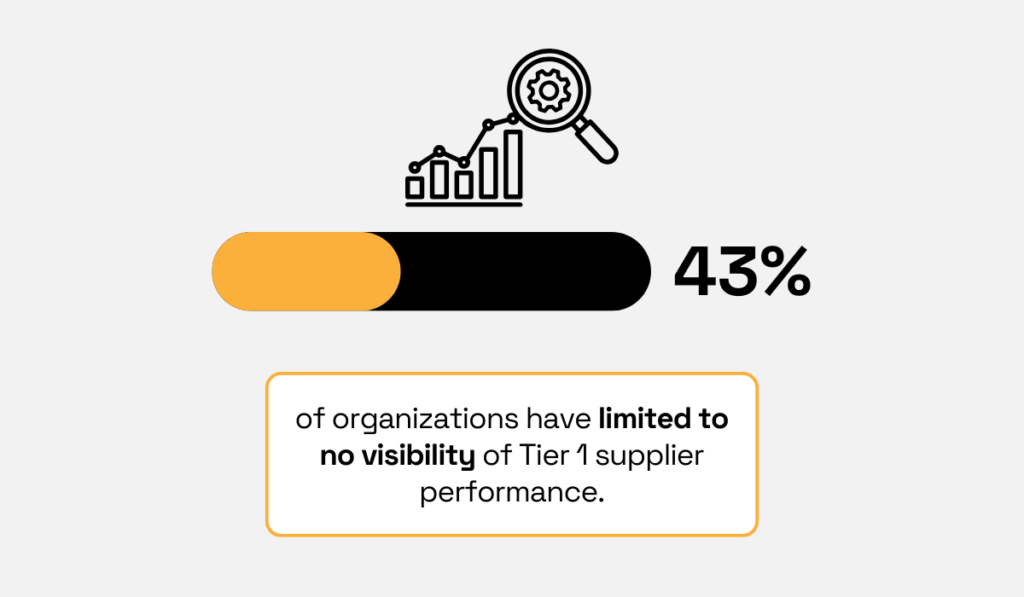
Illustration: Veridion / Data: KPMG
Lack of performance data impacts overall operations and decision-making, and the risks increase if the suppliers in question are responsible for delivering critical materials and services.
Improving supplier evaluation is, therefore, a vital element of effective procurement strategies, seeing as it helps maintain a profitable and resilient supply chain.
The starting point is to define the relevant supplier performance metrics.
Establishing the right metrics can be challenging, but it’s much easier when you keep in mind key assessment areas:
Supplier quality metrics typically form the basis for ongoing evaluation.
However, the only way to categorize suppliers based on their strategic impact and supply risk is by covering all the assessment areas.
Now you’re probably wondering which tools can help you analyze and present supplier data.
Mohammed Abdul Ghafoor, an Engineering Manager at Confidential, emphasizes the pivotal role of both segmentation matrices and performance scorecards.

Illustration: Veridion / Quote: LinkedIn
Scorecards are generally used for both supplier selection and performance monitoring, helping organizations create and maintain a thorough supplier portfolio.
Different Excel sheet templates can help you capture performance insights within your database, but dedicated vendor management solutions like Gatekeeper offer more flexibility when it comes to data presentation.
As shown below, visualizing performance trends makes it easier to compare results across several evaluation areas and quickly identify weak points.
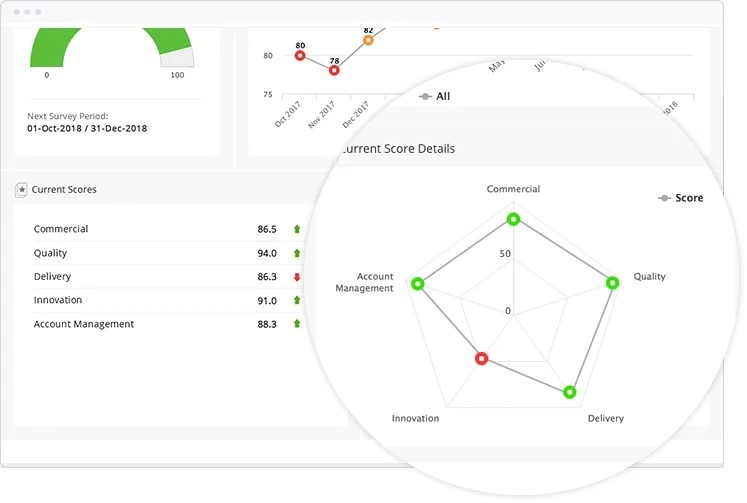
Source: Gatekeeper
Whichever your preferred solution may be, make sure not to skip this step if you want to create a comprehensive supplier database.
Automating data updates ensures you have ongoing access to relevant and accurate supplier information.
After all, the effectiveness of your supplier database depends on good data management practices.
However, the reality is that many businesses struggle to keep supplier information up-to-date and make data-driven decisions in general.
The Hackett Group’s Senior Procurement Advisor, Nicolas Walden, explains that it’s common for organizations to focus on supplier data during the early stages of supplier lifecycle management (SLM), but not after the relationship has been formed.

Illustration: Veridion / Quote: HICX
But why is this the case?
After all, there are plenty of risks to using outdated supplier information, from reduced operational efficiency and missed opportunities to compliance issues and financial harm.
A closer look at some of TealBook’s findings offers several possible explanations, including the lack of automation technology.
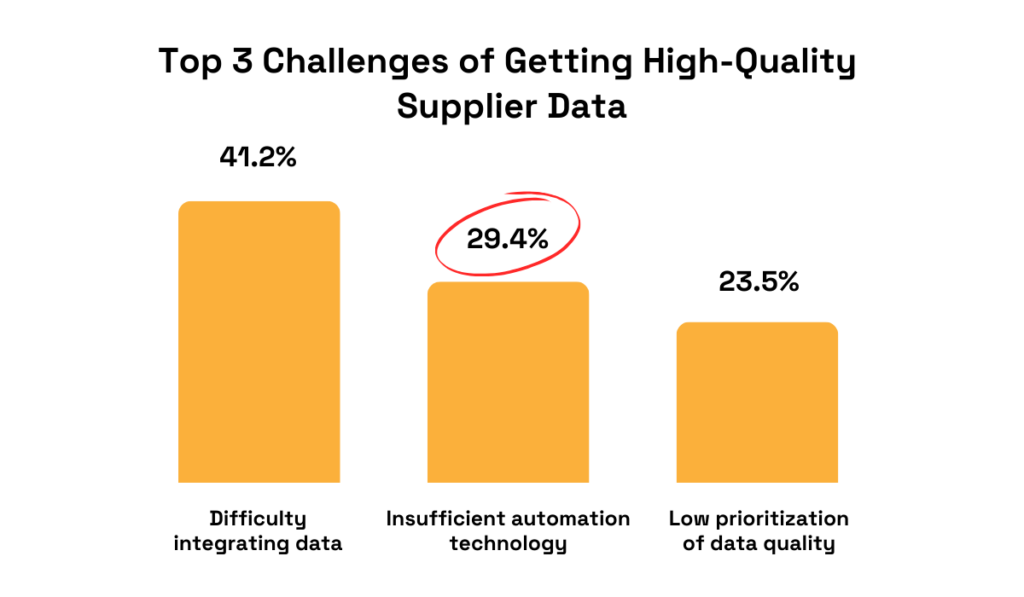
Illustration: Veridion / Data: TealBook
With nearly 30% of respondents citing the lack of automation technology as a major factor impacting data quality, it’s clear that businesses can no longer manage hundreds and thousands of suppliers using only manual processes.
Implementing automation tools streamlines updates to increase productivity, reduce errors, and ensure regulatory compliance.
Moreover, combining technology and improvement initiatives helps you actively mitigate evolving risks, as pointed out by Richard Burrelle, Director of Procurement Operations for IGM Financial.
Risk remains top of mind for our procurement teams. 2025 will be a year focused on continuing to address risk gaps by utilizing a combination of technology solutions and process improvement initiatives.
Closing risk gaps before they become major issues is an essential part of modern supplier management, but practicing vigilance requires the right tools that deliver more than automation.
Consider Veridion, an AI-powered solution that delivers top-notch data accuracy while accelerating several procurement processes, from sourcing to SRM and risk management.
By using our Match & Enrichment service, you can efficiently refresh outdated information while also:
Here’s a glimpse of Veridion’s advanced matching algorithm in action—one simple inquiry in natural language, and you can quickly verify contact information or enrich supplier profiles.

Source: Veridion
Relying on outdated supplier information introduces unnecessary risks, from compliance issues to supply chain disruptions.
Automating supplier database updates ensures data remains accurate, accessible, and actionable, in turn empowering procurement teams to make informed decisions with confidence.
Securing your supplier data is the final step toward developing an effective supplier database.
A robust supplier database should enable easy access to authorized users, but also integrate best security practices to maintain compliance and protect sensitive information.
Cyber threats pose significant risks in today’s digital landscape, with Allianz risk barometer ranking them as the top business concern in 2024.
The report also highlights that most businesses view data breaches as one of the most severe threats to their operations.

Illustration: Veridion / Data: Allianz
To mitigate these risks, businesses need to implement robust data security practices and procedures.
This typically involves regulating access control, implementing encryption protocols, and ensuring compliance with regulations like GDPR and ISO standards.
When it comes to securing supplier data specifically, policies should address key areas such as:
Additional measures, such as vulnerability assessments and database activity monitoring, are also frequently suggested by industry professionals in online discussions.
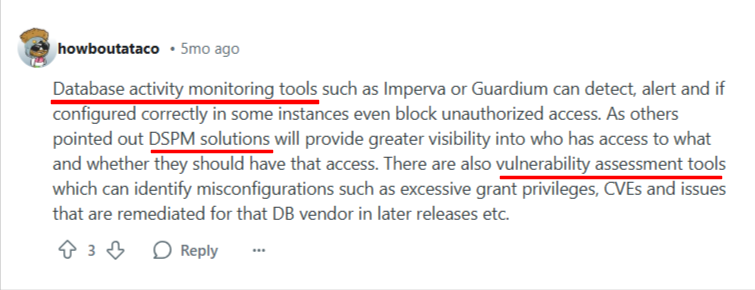
Source: Reddit
However, keep in mind that even with strong security measures in place, no system is entirely immune to data breaches.
That’s why training both staff and suppliers on security policies and procedures is just as crucial as developing them.
Cybersecurity expert Mike Holcomb reinforces this point, emphasizing the importance of not only formulating but actively practicing an incident response plan.

Illustration: Veridion / Quote: LinkedIn
This will ensure a swift, coordinated response to emerging threats, minimizing disruption.
Ultimately, prioritizing data consistency and a high degree of preparedness helps companies securely store vast amounts of information while maintaining supplier trust.
Building a well-structured supplier database is crucial for improving supplier visibility, optimizing procurement processes, and securing long-term success in a dynamic market.
The process involves several steps, but it ultimately comes down to two things: prioritizing data that aligns with your objectives and ensuring ongoing database reliability.
Technology plays a key role in turning fragmented supplier information into a strategic asset, enabling better performance monitoring and process automation for greater efficiency.
Now is the time to assess your approach—how well does your current database support your goals, and what’s the one thing you would change about it?