7 Examples of Successful Supplier Sourcing Strategies

Supplier sourcing—finding, evaluating, contracting, and managing suppliers—is key to driving successful company operations.
In today’s market, companies use various sourcing strategies to ensure their suppliers align with business goals, from sustainability to innovation.
In this article, we’ll explore how seven industry leaders have leveraged specific sourcing strategies to enhance their operations.
For each company, we’ll highlight one or more focus areas that have been critical to their growth and supply chain resilience.
Let’s start.
PepsiCo is a global leader in the beverage, food, and snack industry that needs no further introduction.
The vision of making PepsiCo’s products available “always everywhere” has been a key driver of the company’s business success.
While PepsiCo’s sourcing strategies and policies cover all essential aspects of supplier sourcing, we’ll focus on two main areas:
With a vast network of suppliers across more than 100 countries, PepsiCo has historically prioritized sourcing ingredients locally, which helps keep supply costs low.
Of course, adherence to PepsiCo’s Supplier Code of Conduct (SCoC) is a crucial condition for doing business with the company.
In addition, suppliers are expected to comply with a range of other sustainability policies relevant to them.
To illustrate, here’s a list of those policies:

Illustration: Veridion / Data: PepsiCo
With all the principles, guidelines, and commitments that PepsiCo suppliers need to follow, finding and evaluating new suppliers can be a complex and challenging task.
PepsiCo’s procurement teams must ensure that prospective suppliers meet specific criteria, including price, quality, and delivery parameters.
On top of that, they have to find suppliers that will comply with strict sustainability and ethical standards.
The same goes for PepsiCo’s existing suppliers, whose compliance must be continuously monitored.
So, how does PepsiCo tackle these challenges?
The answer lies in digital innovation.
PepsiCo has been steadily adopting cutting-edge digital technologies to streamline its supplier-sourcing workflows.
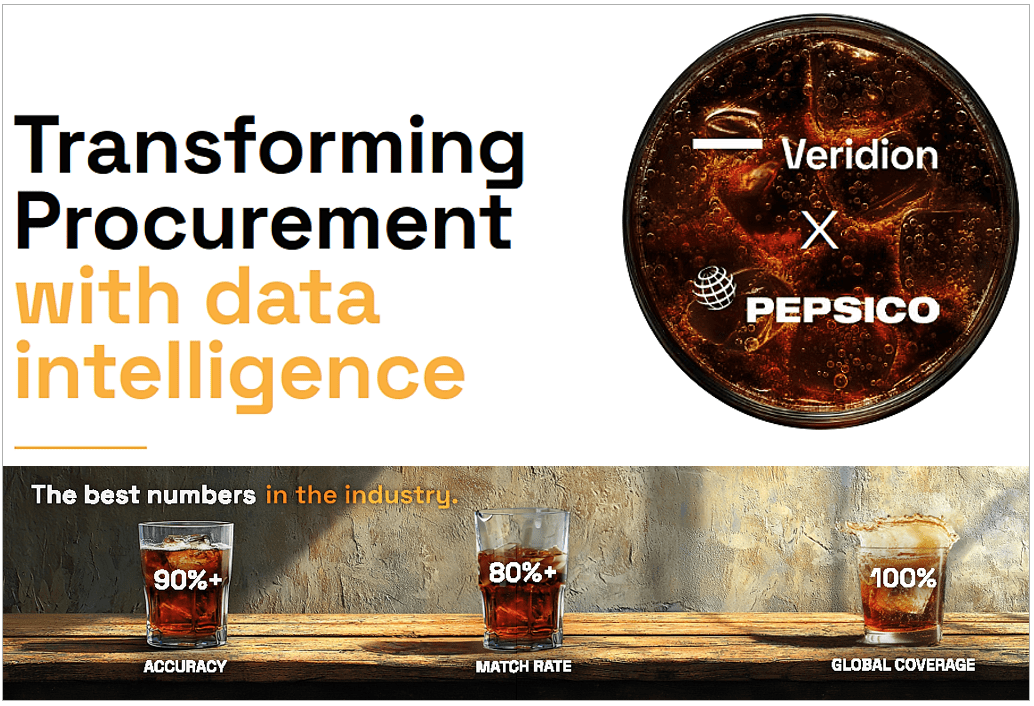
One of these tools is our Veridion, a leading global provider of procurement data.
Veridion provides PepsiCo with AI-powered, weekly-refreshed supplier data and market intelligence.
This data is a foundation for PepsiCo’s sourcing decisions.
Source: CPO Strategy
Veridion’s AI-driven algorithms constantly scour the internet to collect and classify data about all companies with an active digital presence.
The resulting database is updated weekly.
It currently includes over 100 million companies around the globe with more than 750 million products and services tracked across 70+ data attributes.
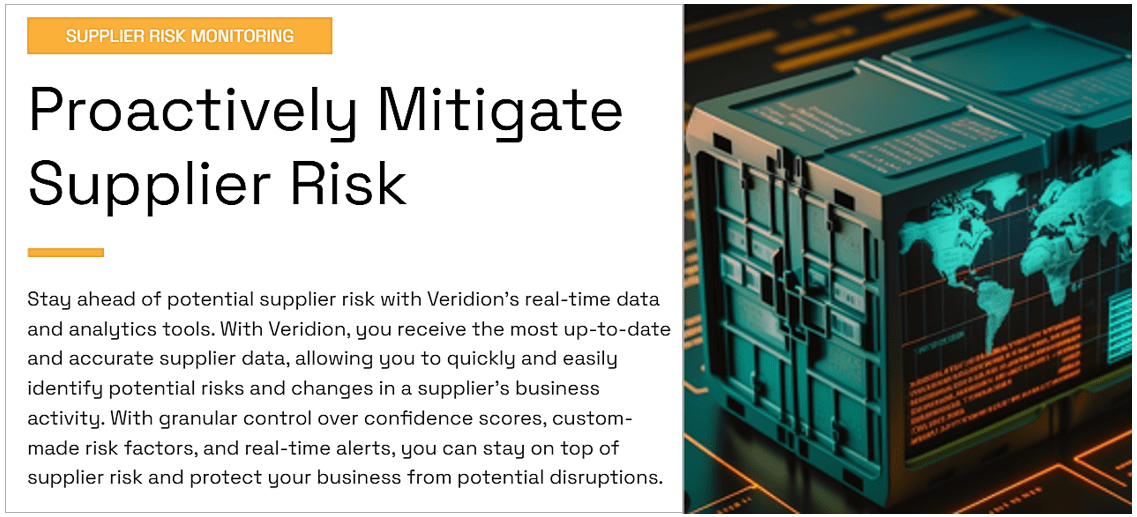
Together with its advanced search functions, Veridion’s database allows procurement teams to:
Source: Veridion
Clearly, PepsiCo can leverage Veridion’s supplier data and market intelligence for various sourcing functions, from fast supplier discovery to proactive risk monitoring.
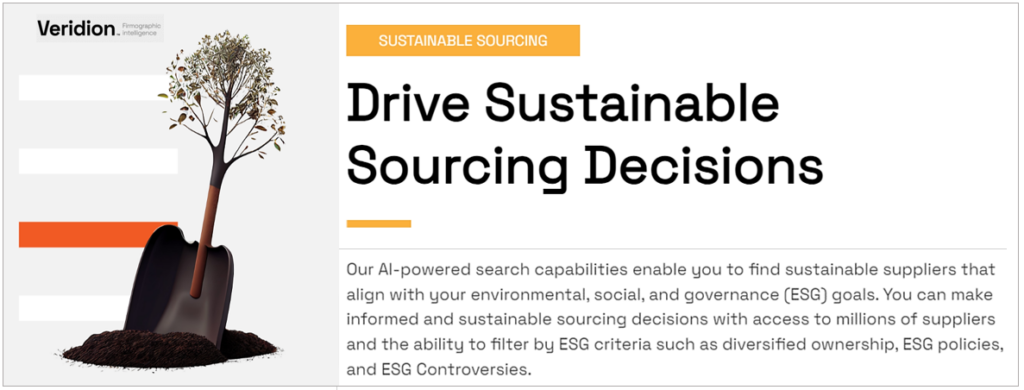
Another feature that assists PepsiCo in its local sourcing and sustainable agriculture efforts is the ability to filter potential suppliers for environmental, social, and governance (ESG) commitments, policies, and controversies.
Source: Veridion
The combination of these functionalities—along with Veridion’s unmatched data accuracy and global coverage—is what led PepsiCo to partner with Veridion.
Currently, this strategic partnership focuses on gathering data to help PepsiCo achieve its sustainability and climate goals, especially in agriculture and packaging.
Of course, PepsiCo employs a range of other digital tools to streamline sourcing procedures, enhance supply chain visibility, and leverage data analytics.
All these systems also benefit from access to Veridion’s comprehensive, up-to-date supplier data.
With these technologies integrated across its global supply chain, PepsiCo is well-positioned to maintain its commitment to sustainable agriculture and local sourcing while continuing to drive business success.
Apple, an electronics giant, is another company whose more detailed introduction is not necessary.
The company ships over 400 million products every year, with about 250 million of those being iPhones.
Each Apple product is a testament to a truly globalized supply chain, with components coming from around the world.
When sourcing suppliers, Apple uses a rigorous selection process.
It focuses on key factors like quality standards, cost-effectiveness, and sustainability practices.
This commitment to selecting and working with top-tier suppliers is reflected in the company’s spend data, shown below:

Illustration: Veridion / Data: CPO Strategy
Apple can rely on a smaller number of top suppliers because the company’s high demand allows these suppliers to dedicate much or all of their operations to fulfilling Apple’s orders.
From there, Apple uses its scale and purchasing power to establish strict manufacturing and sustainability standards across its supply chain.
Among other things, these standards include a zero-tolerance policy for debt-induced labor, a ban on working hours violations, and sustainable practices for sourcing raw materials.
Innovation is another key pillar of Apple’s supplier strategy.

Source: Apple
The company provides incentives for suppliers who innovate or exceed their performance metrics.
Suppliers who do so may ultimately receive more orders or long-term contracts, motivating them to invest in new technologies and processes.
For example, Apple’s focus on sustainability drives suppliers to innovate in areas like material sourcing and waste reduction.
Overall, Apple’s approach to supplier sourcing ensures consistent product quality and fosters strong, long-term supplier relationships.
These partnerships drive continuous performance improvements, reinforcing Apple’s leadership in both technological innovation and sustainability.
L’Oréal is a well-known multinational cosmetics manufacturer that integrates strong ethical and sustainability principles into its supplier sourcing practices.
The company has made environmental and social performance a key criterion for selecting and evaluating suppliers.
This journey began in 2002 with the L’Oréal Buy & Care program, which introduced responsible purchasing policies.
Twenty years later, in 2022, the company further strengthened its standards by launching a new sustainable sourcing strategy built around four key pillars:
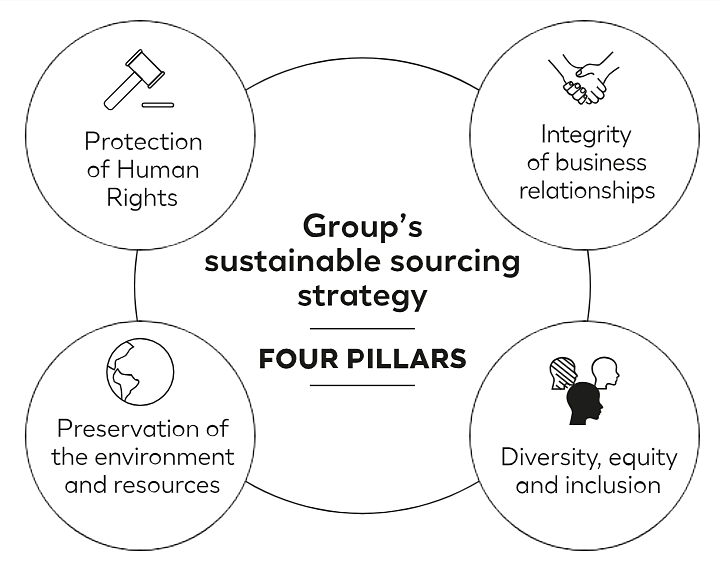
Source: Loreal Finance
The values and standards in these pillars—along with related commitments, objectives, and monitoring tools—are shared with L’Oréal’s suppliers.
In addition to these values, the company’s sustainable sourcing policy also includes traditional supplier performance criteria such as:
This common framework enables L’Oréal to establish a global supplier scoring system across all procurement areas.
Within this system, compliance with corporate social responsibility (CSR) commitments accounts for 20% of a supplier’s final assessment score.
Using these global scorecards, L’Oréal has evaluated and selected 97% of its strategic suppliers based, in part, on their environmental and social performance.
Simply put, L’Oréal leads the way in integrating ESG and CSR criteria into supplier sourcing.
It ensures the selection of suppliers who adhere to strict ethical and sustainable practices.
IKEA, a furniture and home accessories giant, sets an example of a successful supplier-sourcing strategy.
It combines the cost benefits of its scale with a strong focus on local sourcing and environmental sustainability.
More specifically, IKEA’s global operations scale allows it to achieve cost-efficient and sustainable production and procurement while also leveraging local suppliers’ regional expertise and materials.
As such, IKEA’s localized supply chain strategy goes beyond sourcing locally and strives to embed the company’s operations in local communities by:
Moreover, IKEA is committed to building long-term partnerships with its suppliers.
This commitment shows in the average duration of these relationships, illustrated below:

Source: IKEA
Given all the above, IKEA’s focus on sourcing locally and tailoring its product offerings to regional markets provides several strategic advantages, including:
The backbone of IKEA’s supplier sourcing strategy is its Supplier Code of Conduct, better known as IWAY (IKEA Way on Purchasing Products, Materials, and Services).

Source: IKEA
Originally established in 2000, IWAY has evolved over the years, incorporating new sustainability standards and best practices.
The latest version, IWAY 6, launched in 2020, expands on topics such as animal welfare, biodiversity protection, and natural resource conservation.
It also shifted the procurement audit focus from simply verifying compliance to actively helping suppliers improve worker competencies and operational efficiency.
To recap, IKEA stands out for its ability to integrate local sourcing and environmental sustainability principles with the cost-efficiency of its global scale.
The result is a resilient and adaptive supply chain that supports both business and community growth.
As a global leader in healthcare products, Johnson & Johnson prioritizes all the key areas of supplier sourcing you would expect.
This includes selecting suppliers who offer competitive pricing, deliver high-quality products, drive innovation, and uphold ethical and environmental standards.
However, in this section, we’ll focus on how J&J approaches supplier diversity within its global supply chain.
J&J recognized the importance of supplier diversity back in 1998 when the company established its Global Supplier Diversity & Inclusion program.
This program aims to attract small businesses, social enterprises, and minority-owned companies to become J&J’s suppliers.
Since they’ll be selected on merit like all other suppliers, interested businesses must first register at J&J’s supplier portal.
Source: JNJ Supplier One
For those who don’t meet initial standards, J&J offers mentoring programs that can help them improve their operations so they can meet procurement requirements in the future.
Additionally, J&J invested in programs that increase the visibility of small and diverse suppliers on its purchasing platform or match suppliers with different buyers.
Over the past 25 years, this program has expanded across more than 20 markets, and in 2023, J&J’s spend with small and diverse suppliers reached $4.9 billion.
Here are some other figures about J&J’s diversity spend:
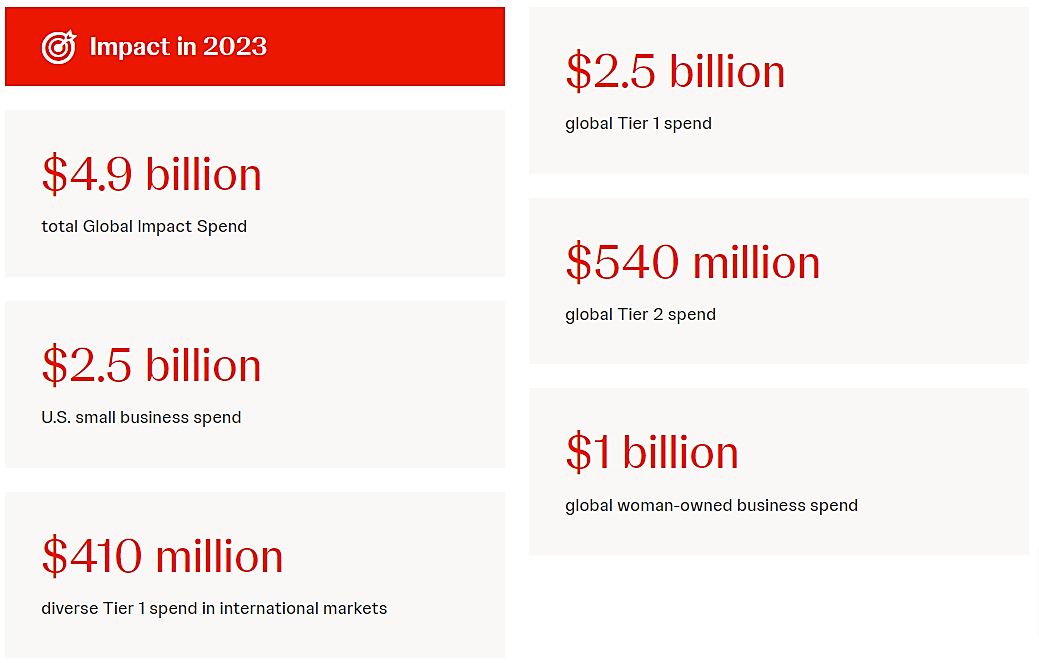
Source: Johnson & Johnson
Given the scope of J&J’s spend involving diverse suppliers, it’s clear that J&J’s DEI program has brought the company a wealth of new ideas and innovative solutions.
At the same time, this reinforces J&J’s commitment to making a positive social impact by promoting economic growth and opportunity for underrepresented communities.
Walmart has built a reputation as a low-cost retail leader, largely due to its effective supplier negotiation strategies and long-term partnerships.
Since its foundation in 1962, Walmart has used its now globally recognized everyday low price (EDLP) strategy.
This approach centers on consistently offering low prices to consumers rather than relying on frequent sales and discounts.
A crucial element of this strategy is Walmart’s direct sourcing model, which eliminates intermediaries, allowing the company to negotiate prices directly with manufacturers.
Local sourcing is another key element of this strategy.
For example, in Walmart’s home market (the US), over two-thirds of products are either made, grown, or have components assembled within the country.
As Walmart’s head of global sourcing, Andrea Albright explains:

Illustration: Veridion / Data: FDI Intelligence
Recognizing the cost advantages of local sourcing, Walmart has committed to investing $350 billion in US-based, locally sourced products by 2030.
In addition, Walmart plans to apply the same local sourcing approach in other major markets.
For example, the company has pledged to source at least $10 billion of local products annually in India by 2027.
Another key element of Walmart’s low-cost strategy is its private label brands, such as Great Value, Sam’s Choice, and Equate.
These brands allow Walmart to reduce production costs for suppliers while offering consumers affordable alternatives to name-brand products.
In summary, Walmart optimizes its EDLP strategy through direct negotiations with manufacturers, prioritizing local sourcing, and maintaining long-term supplier relationships.
Toyota is well-known for its Just-In-Time (JIT) sourcing practices and strong supplier relationships, both of which are central to its lean production model.
The JIT philosophy focuses on producing only what is needed, when it is needed, and in the exact amount required.
This system minimizes inventory levels, reduces waste, and lowers storage costs by synchronizing production with demand.
The JIT concept is the cornerstone of the renowned Toyota Production System (TPS), which has become a model for “lean” production approaches across various industries.
Source: Toyota
When applied to sourcing, the JIT system demands precise coordination, real-time communication, and a high level of trust between Toyota and its suppliers.
This is why Toyota prioritizes building long-term partnerships with its suppliers, fostering collaboration and mutual development.
Toyota supports its suppliers by offering long-term contracts, giving them the security to invest in technology and process improvements.
It also enhances their capabilities through development programs and best practice-sharing initiatives.
This focus on close, cooperative relationships has redefined supply chain dynamics, shifting from simple transactions to proactive partnerships.
However, JIT sourcing comes with challenges.
For example, errors in Toyota’s parts order management system halted production across 14 plants.
Source: Forbes
Additionally, recurring shortages of key components like semiconductors have forced some companies to adapt JIT into a Just-In-Case (JIC) model, building larger safety stock reserves to avoid disruptions.
Toyota’s approach exemplifies a sourcing strategy that builds enduring partnerships, bringing mutual benefits to both sides.
Yet, recent challenges highlight the need for flexibility and contingency planning, even within the most efficient systems.
We hope these seven examples have shed light on key aspects of successful supplier-sourcing strategies across various industries.
The areas we focused on cover a range of strategies, including local sourcing, sustainability, innovation, supplier diversity, low-cost sourcing, and JIT.
When carefully selected and properly implemented, one or more of these sourcing tactics can help your company enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and build stronger supplier relationships.
Of course, this requires a methodical, strategic approach supported by the right tools that facilitate sourcing processes, from supplier discovery and procurement management to data analytics.
Take inspiration from these examples, equip your team with the right tools, and start building a robust sourcing strategy that sets your business up for long-term success.