How to Conduct a Procurement Audit in 7 Steps

Regardless of their size and industry, companies face unique challenges in managing their procurement processes, from identifying and vetting suppliers to ensuring compliance with contracts and regulations and optimizing supplier relationships.
With so many moving parts, it’s likely that some red flags may go unnoticed.
That’s why companies rely on procurement audits to evaluate their practices, identify areas for improvement, and drive cost savings.
In this article, we’ll explore seven essential steps involved in conducting a procurement audit, along with practical tips to guide you through the process.
For a procurement audit to be effective, the first step is to determine what you want to achieve.
This starts by outlining the general objectives of an audit and then determining specific aspects of procurement processes you want to focus on.
The overarching goals of a procurement audit typically include:
Although they’re a good starting point, these goals are still too general to be useful in helping you define more specific audit objectives.
Things become clearer if we broadly classify them into:
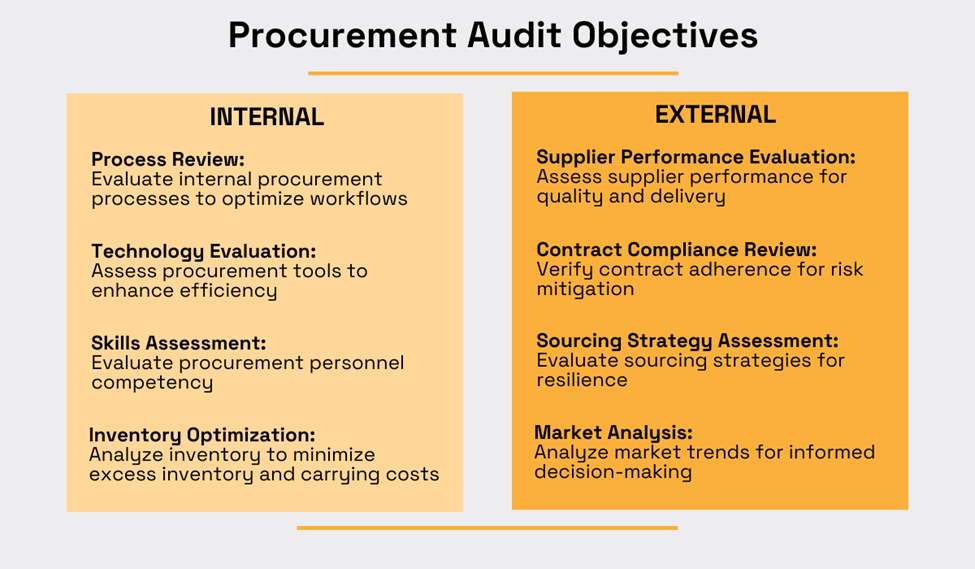
On that note, here is a more granular overview of a procurement audit’s general objectives:
Source: Veridion
These more specific but still general objectives illustrate the multifaceted nature of a comprehensive procurement audit, addressing both internal processes and external relationships crucial to the success of procurement operations.
That’s why some companies opt to do internal and external procurement audits separately or to focus an audit on specific problem areas.
This is where gathering insights from key stakeholders comes in.
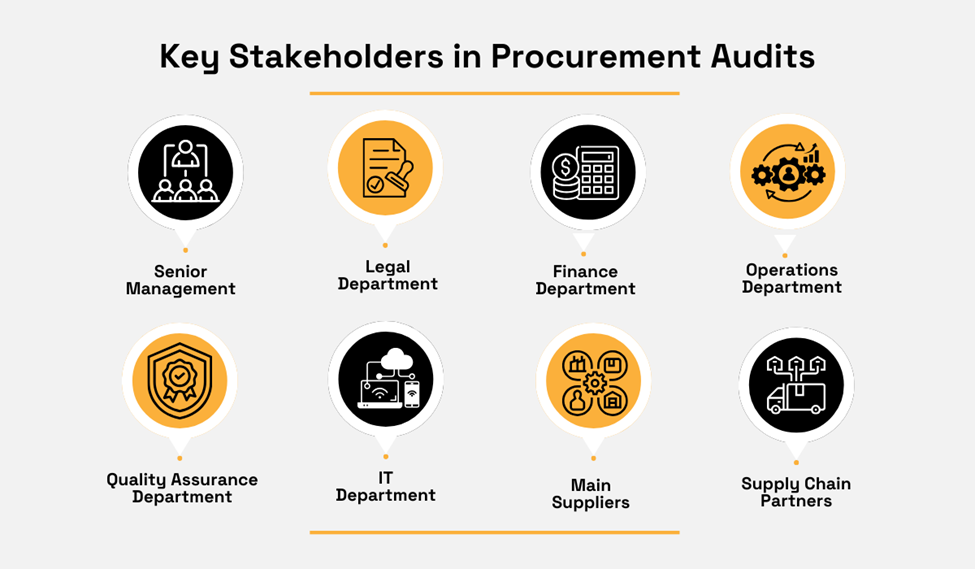
Key stakeholders typically include members of senior management relevant to procurement, as well as competent representatives from finance, legal, operations, quality assurance, and IT departments.
Source: Veridion
As illustrated, consultations with main suppliers and other supply chain partners (distributors, logistics providers, etc.) can also provide valuable input on specific issues, inefficiencies, and bottlenecks within procurement processes and supply chain operations.
The insights obtained from these stakeholders can be crucial in identifying audit priorities, understanding operational challenges, and ensuring that audit objectives are aligned with organizational goals.
To recap, the initial step in conducting a procurement audit is to define the general objectives and then refine them by leveraging stakeholder input.
With a clear understanding of your procurement audit objectives, you can move to assembling an audit team.
The composition of your audit team depends on various parameters, including whether the audit will be conducted by internal employees, external auditors, or a combination of both.
Additionally, factors such as the size of your company, the scope of its procurement data, and the defined audit objectives play crucial roles in assembling the team.
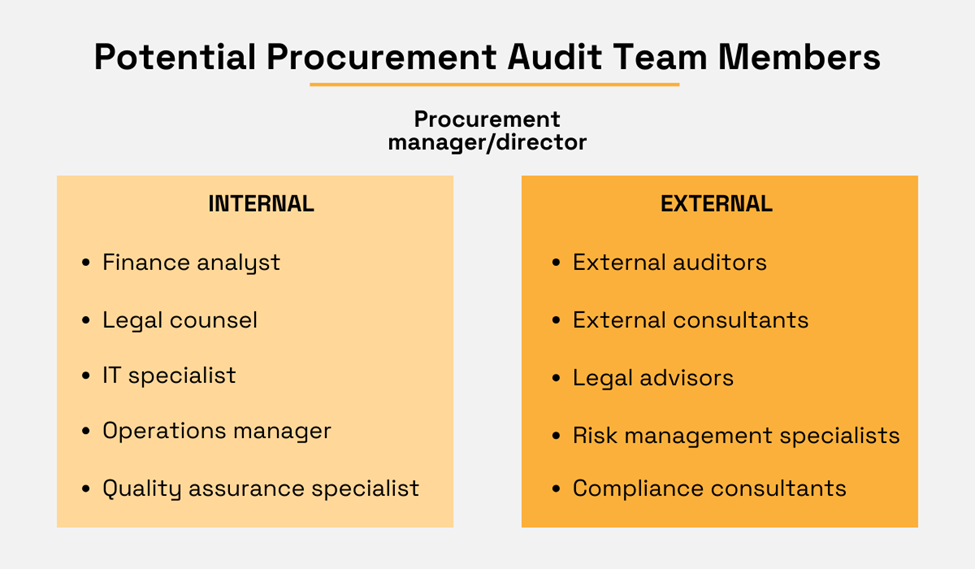
What can be said with certainty is that the team should comprise individuals with diverse expertise in procurement, finance, auditing, and other relevant areas.
To illustrate, here are some potential internal and external members of an audit team.
Source: Veridion
If your team is going to be fully internal, make sure to avoid possible conflicts of interest where audit team members review their own procurement procedures and contracts, which can lead to skewed results and oversights.
Moreover, collaboration between internal and external audit team members can bring diverse perspectives, industry knowledge, and best practices to the audit process.
This will, in turn, enhance its effectiveness and ensure comprehensive coverage of procurement activities.
Once the team setup is decided, it’s crucial to assign clear roles and responsibilities, balancing the internal team members’ auditing tasks with their ongoing procurement workload.
Along with a clear division of tasks and duties, establishing clear communication channels and scheduling regular meetings of the audit team are essential for effective collaboration and coordination.
To recap, assembling a well-rounded audit team with diverse expertise and clear roles ensures a thorough evaluation of procurement processes, fosters collaboration, and lays the foundation for a successful procurement audit.
Examining the procurement documents is a critical phase of the procurement audit process.
It provides valuable insights into your organization’s procurement practices, contract management, and compliance with policies and regulations.
These documents serve as tangible evidence of procurement activities and can help identify areas for improvement, potential risks, and opportunities for cost savings.
As such, they offer a comprehensive view of the procurement lifecycle, from the initial requisition of goods or services to payment and contract renewal.
Here are some key documents that should be examined during a procurement audit:
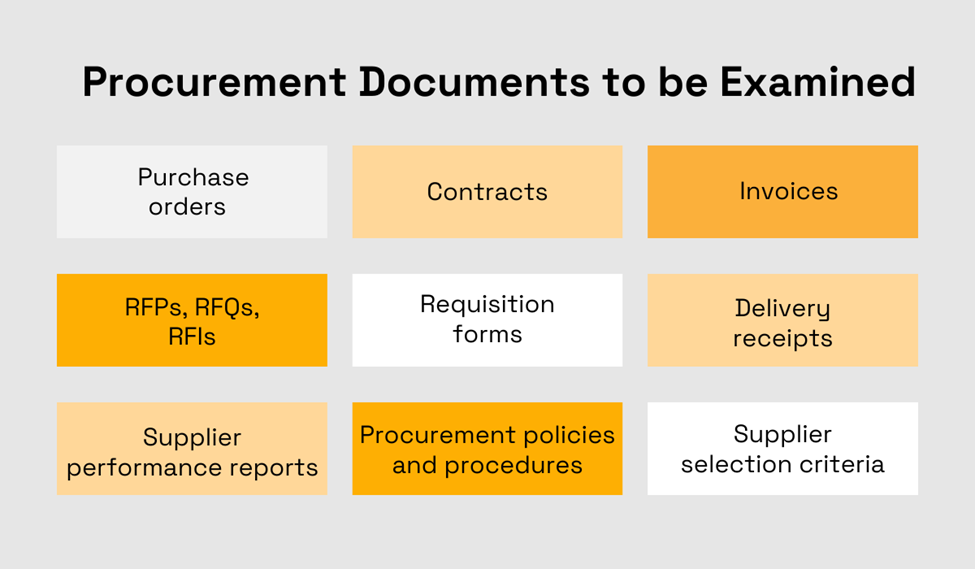
Source: Veridion
During this phase of the audit, it’s essential to review each document thoroughly, paying attention to details such as:
Depending on the volume of procurement within your company, examining every single document may be unrealistic.
In such cases, you can select a manageable portion of these documents as an auditing sample while ensuring that each document type is represented.
Other practical tips for examining procurement documents include:
During this phase, you should instruct team members to look for missing info, discrepancies, inconsistencies, or deviations from established procedures, as these may indicate areas of concern that require further investigation.
All in all, examining the procurement documents is essential for ensuring that all transactions are adequately documented and compliant with your organization’s policies and procedures.
The document examination phase continues with the review of your supplier relationships.
During this phase, it’s essential to assess the effectiveness of selection criteria used for supplier evaluation, ensuring alignment with organizational goals and objectives.
Furthermore, the audit team should gauge the performance of your suppliers and identify areas for improvement by evaluating metrics such as:
In addition to embracing technology to organize documents and procedures internally, you should consider leveraging external sources of supplier data that allow you to benchmark your suppliers against others on the market.
For instance, our supplier sourcing and risk management tool, Veridion, includes a global, regularly updated database of supplier information and powerful search services that are easily integrated with other procurement tools you’re using.

Source: Veridion
With Veridion’s Match & Enrich API, you can easily update your own supplier records, ensuring that any unreported or emerging issues with your suppliers are immediately detected.
Likewise, you can leverage our Complex Search API to quickly find other similar suppliers, so you can benchmark them against the pricing and performance of your current suppliers.
To do that, you can use natural language input, like in this example.

Source: Veridion
Benchmarking your suppliers against those found by Veridion enables you to assess the effectiveness and competitiveness of your organization’s supplier selection practices, identify areas for improvement, and negotiate better terms with suppliers going forward.
Moreover, you can use Veridion to set up automatic real-time alerts for any risk factors you find relevant, thus ensuring you’ll be timely notified if one of your suppliers is faced with such risks.
Overall, embracing internal and external technology tools can make the process of reviewing your supplier relationships much easier, faster, and more accurate.
This can empower your audit team to detect supplier-related issues and suggest appropriate actions with more ease.
In parallel with reviewing supplier relationships, the audit team should assess your procurement team’s practices, too.
This will allow you to identify areas for improvement, such as streamlining workflows, reducing costs, or enhancing transparency.
This step also involves verifying that your procurement authorization procedures and internal controls have the necessary checks and balances in place to prevent fraud, minimize errors, and reduce risks.
As the below article shows, even the biggest companies can fall prey to fraudulent activities (such as impersonating their existing supplier) due to poor internal procedures.
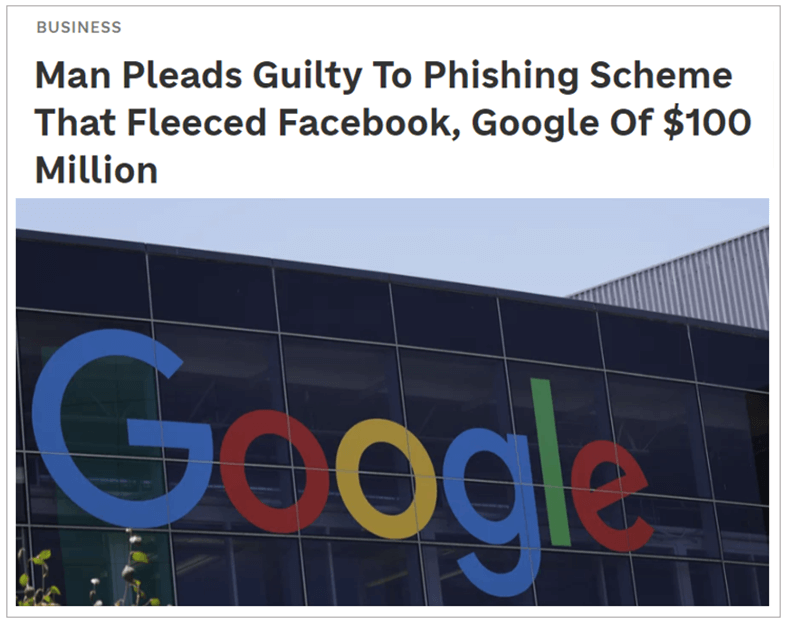
Source: NPR
The fraudster in question created a dummy company and fake emails and invoices to convince Google’s and Facebook’s procurement functions that they’re doing business with their current supplier, leading them to make a series of payments to false bank accounts.
This example illustrates the importance of analyzing your procurement practices to identify weaknesses in authorization procedures and internal controls.
Other than fraud prevention, reviewing internal procurement practices allows you to optimize operational efficiency and streamline workflows by identifying bottlenecks, redundancies, and inefficiencies in your processes.
This audit step can also help enhance overall transparency, accountability, and compliance within your organization.
To efficiently analyze your procurement practices, consider the following actions:
These tips should enable you to streamline the processes involved in this audit step, making it easier to identify areas for improvement, enhance operational efficiency, and ensure compliance with industry standards and best practices in procurement.
Performed in close collaboration with the finance department, this step in your procurement audit should enable you to identify rogue spending.
In short, rogue spending refers to any instances of unauthorized or non-compliant purchases that occurred outside of established procurement processes.
Identifying such instances involves closely examining your company’s expenditure against procurement records and transactions, allowing you to detect irregularities and deviations from established policies and procedures.
The audit team members should look for patterns of rogue spending, such as off-contract purchases or excessive spending by certain departments or individuals.
For instance, several departments might be using different-priced vendors for office supplies or even procure them from the same vendor at different prices.
Of course, rogue spending is much easier to identify when all the data is stored, processed, and analyzed by spend management software.
You can see one such tool in the image below:
Source: Procurify
Other than implementing spend analytics tools, the audit team members should also conduct interviews with key stakeholders to gather insights into spending practices and identify any unauthorized purchases.
When data analysis meets personal insights, it’s easier to identify instances of rouge spending and address their root causes, which often reveals opportunities for cost savings through better spend control and enhanced supplier management.
In short, this phase of your procurement audit focuses on uncovering hidden sources of financial leakage and putting them under the control of the procurement function, ultimately resulting in cost savings and efficiency gains.
The final step in the procurement audit process is to compile the findings, recommendations, and supporting evidence into a comprehensive audit report.
This report serves as a crucial document summarizing the outcomes of the audit, including identified strengths, weaknesses, and opportunities for improvement within the procurement process.
It should provide a detailed analysis of the audit findings, highlighting areas of concern, potential risks, and suggested corrective actions.
To illustrate how an audit report can be structured, consider the table of contents of an external audit report on the procurement practices of the New York City Law Department:
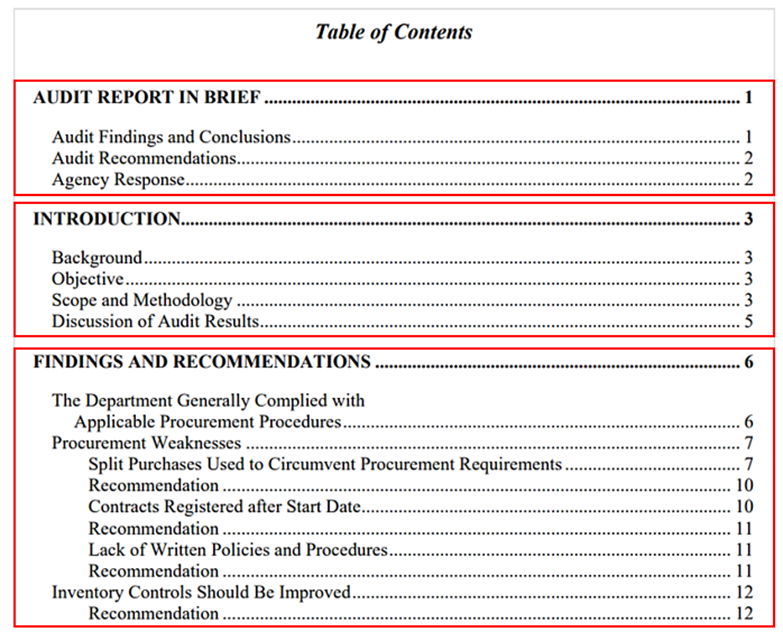
Source: nyc.gov
As you can see, the report is logically structured.
It starts with an executive summary, moves to explain the audit objectives, scope, and methodology, and then provides detailed findings and actionable recommendations.
Moreover, procurement audit reports should be written in clear and concise language.
This is going to make it easy for stakeholders to understand the findings and take appropriate actions to address identified issues.
Of course, the report, i.e., the results of the audit should be clearly communicated to relevant stakeholders, such as senior management, finance, procurement teams, and other key decision-makers.
This will ensure company-wide transparency and accountability, facilitating informed decision-making and driving organizational improvements in procurement practices.
In closing, conducting regular procurement audits is vital for companies that want to evaluate and improve their procurement practices.
Although the auditing process does involve some complexities, these can be efficiently addressed by leveraging appropriate software tools and data analysis methodologies.
When properly conducted and transparently communicated, procurement audits can help companies identify areas for improvement, enhance efficiency, and drive cost savings.